
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


L
LAN-Modem
Description: A profile created by the system for each installed modem card.
Usage: Use the Read and List commands to make LAN-Modem the working profile and list
its contents. For example:
admin> read lan {1 6 0}
LAN-MODEM/{ shelf-1 slot-6 0 } read
admin> list
physical-address*={ shelf-1 slot-6 0 }
modem-disable-mode=[ enable enable enable enable enable enable +
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the profile. To close the profile and save your changes:
admin> write
LAN-MODEM/{ shelf-1 slot-6 0 } written
Dependencies: The LAN-Modem profile exists until a different slot card is detected in the
slot. Removing or downing a modem card does not delete the profile or change its contents.
See Also: Modem-Disable-Mode, Physical-Address
Layer3-End
Description: Specifies CCITT Layer 3, which must be set to its default when a DPNSS or
DASS2 switch type is in use.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- X-Side (the default) specifies that Layer 3 favors the outgoing call when a call collision occurs.
- Y-Side specifies that Layer 3 does not favor the outgoing call when a call collision occurs.
Example: set layer3-end=x-side
Location: E1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface
See Also: Line-Interface, Switch-Type
Left-Status
Description: Specifies the default content of the left side of the status window.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- Session-List specifies that the MAX TNT displays current system administration sessions on the left side of the status window.
- Connection-List specifies that the MAX TNT displays current system WAN sessions on the left side of the status window.
Example: set left-status=connection-list
Location: User name
See Also: Bottom-Status, Default-Status, Top-Status
Len
Description: Specifies the number of bytes to test in a frame. Starting at the specified Offset,
the MAX TNT compares the contents of the bytes to the generic filter's Value setting.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 8. The default is 0 (zero), which specifies that the MAX
TNT does not compare packet contents and that all packets match the filter.
Example: offset=2
len=8
more=no
comp-neq=no
mask=0f:ff:ff:ff:00:00:00:f0:00:00:00:00
value=07:fe:45:70:00:00:00:90:00:00:00:00
In this Gen-Filter specification, the filter applies the mask to the eight bytes following the two-byte offset.
Location: Filter filter-name > Input-Filters > Gen-Filter,
Filter filter-name > Output-Filters > Gen-Filter
See Also: Gen-Filter, Input-Filters, Output-Filters
Line-Config
Description: A subprofile containing line configuration options for a Serial WAN, RADSL,
or SDSL card.
Usage: With ADSL-Cap, SDSL, or SWAN as the working profile, list the Line-Config
subprofile. For example:
admin> list line
trunk-group=0
nailed-group=2
activation=static
call-route-info={ any-shelf any-slot 0 }
max-down-stream-rate=2560000
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: ADSL-Cap {shelf-N slot-N N}, SDSL {shelf-N slot-N N},
SWAN {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Activation, Call-Route-Info, Max-Down-Stream-Rate, Nailed-Group, Trunk-Group
Line-Interface
Description: A subprofile containing T1 PRI, E1 PRI, or ISDN BRI line configuration
options.
Usage: With a T1 profile as the working profile, list the Line-Interface subprofile. For
example:
admin> list line
enabled=no
frame-type=d4
encoding=ami
clock-source=eligible
clock-priority=middle-priority
signaling-mode=inband
robbed-bit-mode=wink-start
default-call-type=digital
switch-type=att-pri
nfas-id=0
call-by-call=0
data-sense=normal
idle-mode=flag-idle
fdl=none
front-end-type=dsx
DSX-line-length=1-133
CSU-build-out=0-db
channel-config={ { switched-channel 9 "" { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 +
maintenance-state=no
sendDisc-val=0
hunt-grp-phone-number-1=""
hunt-grp-phone-number-2=""
hunt-grp-phone-number-3=""
With an E1 profile as the working profile, list the Line-Interface subprofile. For example:
admin> list line
enabled=yes
frame-type=g703
clock-source=eligible
clock-priority=middle-priority
signaling-mode=isdn
switch-type=net5-pri
front-end-type=short-haul
channel-config=[ { unused-channel 9 "" { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 } +
layer3-end=x-side
nl-value=64
loop-avoidance=7
number-complete=end-of-pulsing
group-b-answer-signal=signal-b-6
group-b-busy-signal=signal-b-3
group-ii-signal=signal-ii-2
answer-delay=200
caller-id=no-caller-id
With an IDSL profile as the working profile, list the Line-Config subprofile:
admin> list line
line-enabled=yes
answer-number-1=""
answer-number-2=""
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: E1 {shelf-N slot-N N}, IDSL {shelf-N slot-N N}, T1 {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Answer-N (N=1-2), Answer-Delay, Call-By-Call, Caller-ID, Channel-Config,
Clock-Priority, Clock-Source, CSU-Build-Out, Data-Sense, Default-Call-Type,
DSX-Line-Length, Enabled, Encoding, FDL, Frame-Type, Front-End-Type, Group-II-Signal,
Group-B-Answer-Signal, Group-B-Busy Signal, Hunt-Grp-Phone-Number-N, Idle-Mode,
Layer3-End, Loop-Avoidance, Maintenance-State, NFAS-ID, NL-Value, Number-Complete,
Robbed-Bit-Mode, SendDisc-Val, Signaling-Mode, Switch-Type
Line-Length
Description: Specifies the length of the Rx and Tx lines to a DSX-3 Cross Connect.
Usage: Specify either of the following values:
- 0-255 (0 to 255 feet)
- 226-450 (226 to 450 feet)
For a direct connection, double the values.
Location: T3 {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Enabled, Frame-Type, Name, Physical-Address,
Line-Quality
Description: Indicates the line quality (in decibels). For an SDSL interface, a reading of -5dB
or better is required for reliable data transfer.
Usage: The Line-Quality setting is read only.
Location: ADSL-Cap-Statistics {shelf-N slot-N N}, SDSL-Statistics {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Connection-SQ, Far-End-dB-Attenuation, HDLC-RX-CRC-Error-Cnt,
Line-Up-Timer, Physical-Address, RS-Corrected-Errors, RS-Errors, RX-Attenuation, RX-Signal-Present
, Self-Test, Transmit-Power, Up-Down-Cntr
Line-State
Description: Reports the state of a T1 PRI, DS3, ISDN BRI, RADSL, SDSL, or SWAN line.
Usage: The Line-State setting is read only. You cannot set Line-State directly. For a T1 PRI
line, the state can have one of the following values:
For a DS3 line, the state can have the same values as a T1 PRI line (except No-D-Channel). In addition, a DS3 line can have one of the following values:
- Idle-Receive indicates that the line is receiving an idle signal.
- Wrong-Frame indicates that the remote end is configured for a different DS3 application.
For an ISDN BRI line, the state can have one of the following values:
For a RADSL line, Line-State can have one of the following values:
- Disabled indicates that the line is disabled.
- Active indicates that the line is up and operating normally.
For an SDSL or SWAN line, Line-State can have one of the following values:
- Does-Not-Exist indicates that the line is not installed.
- Disabled indicates that the line is disabled.
- Active indicates that the line is up and operating normally.
Example: line-state=active
Location: ADSL-Cap-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}, IDSL-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N},
SDSL-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}, SWAN-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}, T1-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N},
T3-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Channel-State, DS2-State
Line-Up-Timer
Description: Indicates the length of time the line has been in the up state.
Usage: The Line-Up-Timer value is read only. It has the following format:
{hh mm ss}
where hh is the number of hours, mm is the number of minutes, and ss is the number of seconds
Location: ADSL-Cap-Statistics {shelf-N slot-N N}, SDSL-Statistics {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Connection-SQ, Far-End-dB-Attenuation, HDLC-RX-CRC-Error-Cnt, Physical-Address
, RS-Corrected-Errors, RS-Errors, RX-Attenuation, RX-Signal-Present, Self-Test,
Transmit-Power, Up-Down-Cntr
Link-Compression
Description: Specifies the link-compression method for a PPP, MP, and MP+ call.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- None specifies no link compression. In the Answer-Defaults profile, None is the default.
- Stac specifies an Ascend-modified version of draft 0 of the CCP protocol. In a Connection profile, Stac is the default.
- Stac-9 specifies draft 9 of the Stac LZS Compression protocol.
- MS-Stac specifies Microsoft/Stac compression (the method used by Windows95). If the caller does not acknowledge Microsoft/Stac compression, the MAX TNT attempts to use standard Stac compression. If the caller does not acknowledge Stac compression, the link uses no compression.
Example: set link-compression=stac-9
Dependencies: Only PPP, MP, and MP+ links support Link-Compression. Both sides of the
connection must specify the same type of link compression. Otherwise, your setting has no
effect.
Location: Answer-Defaults > PPP-Answer, Connection station > PPP-Options
See Also: PPP-Answer, PPP-Options, VJ-Header-Prediction
Link-Mgmt
Description: Specifies the link management protocol to use between the MAX TNT and the
Frame Relay switch. The Frame Relay administrator or service provider can tell you which
value to use.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- None specifies no link management. The MAX TNT assumes that the physical link is up and that all Data Link Connection Indicators (DLCIs) are active on the physical link. None is the default.
- ANSI-T1.617d specifies the link management protocol defined in ANSI T1.617 Annex D.
- CCITT-Q.933a specifies the link management protocol defined Q.933 Annex A.
Example: set link-mgmt=ansi-t1.617d
Location: Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: DCEN392-Val, DCEN393-Val, FR-Name, Link-Type, N391-Val, N392-Val,
N393-Val, T391-Val, T392-Val
Link-State
Description: Indicates the physical state of the LAN interface.
Usage: The Link-State setting can be Up, Down, or Unknown. The value can only be set by
the Ethernet driver.
- Up specifies that the LAN interface can transmit and receive network traffic.
- Down specifies that the LAN interface cannot transmit and receive network traffic (for example, if the Ethernet cable is unplugged or the Ethernet hub on the interface is down).
- Unknown specifies the shelf-controller Ethernet interface.
Location: Ether-Info {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Interface-Address, Link-State-Enabled, MAC-Address
Link-State-Enabled
Description: Specifies whether the value of Link-State affects the IP routing tables.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes specifies that the MAX TNT deletes routes to an interface when Link-State is Down, and adds them when the interface comes up again.
- No specifies that the MAX TNT routes packets to an interface regardless of the Link-State setting. If the interface is down, the MAX TNT discards the packets. They cannot use an alternative route.
Example: set link-state-enabled=yes
Location: Ethernet {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Link-State
Link-Type
Description: Specifies the kind of logical interface between the MAX TNT and the Frame
Relay network on the data link:
- The UNI (User to Network Interface) is the interface between an end-user and a network endpoint (a router or a switch) on the Frame Relay network.
- A DCE (Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment) is a device that connects the DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) to a communications channel, such as a telephone line.
- A DTE refers to a device that an operator uses, such as a computer or a terminal.
- NNI (Network-to-Network Interface) operation allows the MAX TNT to act as a Frame Relay switch communicating with another Frame Relay switch.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- DCE specifies a UNI-DCE connection. The MAX TNT operates as a Frame Relay router communicating with a DTE device. To the DTE device, MAX TNT appears as a Frame Relay network endpoint.
- DTE specifies a UNI-DTE connection. The MAX TNT operates as a DTE communicating with a Frame Relay switch, and performs the DTE functions specified for link management.
- NNI specifies an NNI connection. The MAX TNT performs both DTE and DCE link management. An NNI configuration allows two separate Frame Relay networks to connect by means of a common protocol.
Example: set link-type=dte
Location: Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: DCEN392-Val, DCEN393-Val, N391-Val, N392-Val, N393-Val, T391-Val,
T392-Val
Loadname
Description: Indicates the name of the software load that was running on a slot that failed.
Usage: The Loadname setting is read only.
Example: loadname=load1
Location: Error
See Also: Index, IP-Address, IS-Post, Shelf, Slot, Stack-Trace, Type, User-Profile, Version
Local-Address
Description: Specifies an IP address for the local side of a numbered-interface connection.
Usage: Specify an IP address in dotted decimal notation. Separate the optional subnet mask
from the address by entering a forward slash. The address must be unique to the connection.
You can assign a fake IP address or an IP address from one of the local subnets. The MAX
TNT accepts IP packets destined for the specified address and treats them as destined for the
system itself. The packets might arrive on any interface, and the destination numbered
interface need not be in the active state. The default is 0.0.0.0, which indicates an unnumbered
interface.
Example: set local-address=10.2.3.4/24
Dependencies: The Local-Address value cannot be an address assigned in an IP-Interface
profile to one of the MAX TNT unit's physical LAN interfaces, nor can it be the IP address of
the shelf-controller Ethernet port.
Location: Connection station > IP-Options
See Also: IP-Options, Remote-Address
Local-Echo
Description: Allows you to configure local-echo mode for a terminal-server session.
Local-echo mode is a line-by-line mode. The line appears as the user types it, but is not transmitted until the user enters a carriage return. If local echo is enabled, the line transmitted is echoed on the local MAX TNT terminal screen.
Local echo allows MAX TNT terminal-server users to connect to nonstandard Telnet ports and programs. If the remote server turns local echo on or off in its option negotiation for a Telnet session, the negotiated setting overrides the value of Local-Echo.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes turns on local echo.
- No disables local echo.
Example: set local-echo=yes
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled, Local-Echo does not apply. A terminal-server
user can override the Local Echo setting from the command line by using the -e
option of the Telnet command.
Location: Terminal-Server > Terminal-Mode-Configuration > Telnet-Options
See Also: Telnet-Options, Terminal-Mode-Configuration
Local-Profiles-First
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT should attempt local authentication before
remote external authentication.
Usage: Specify one of the following settings:
- LPF-Yes (the default) specifies that the MAX TNT first attempts to authenticate the connection with a local profile. If the profile exists and the password matches, the MAX TNT allows the connection. If no local profile exists, or if a local profile exists but the password fails, the MAX TNT tries to authenticate the connection through an external authentication server.
- LPF-No specifies that the MAX TNT first tries to authenticate the connection through a remote authentication server. If the server acknowledges the request, it allows the connection. If the server NAKs the request and remote authentication fails (because no remote profile exists, or a remote profile exists but the password fails), or if the remote authentication server cannot be reached, the MAX TNT attempts to authenticate the connection with a local profile.
- LPF-RNo specifies that the MAX TNT first tries to authenticate the connection through a remote authentication server. If the profile exists and the password matches, the MAX TNTallows the connection. If the server doesn't respond, the MAX TNT checks for a matching local profile. If the server NAKs the request and remote authentication fails, the MAX TNT terminates the connection.
Example: set local-profiles-first=lpf-no
Dependencies: Consider the following:
- If Auth-Type=None, Local-Profiles-First does not apply.
- PAP-Token authentication does not produce a challenge with a local profile. Using a local profile defeats the security of using PAP-Token.
- When you use a local profile, PAP-Token-CHAP brings up one channel, but all other channels fail.
- If the remote end of the connection has ever been authenticated with a challenge, Cache-Token does not work with a local profile. If the remote end has never been authenticated, no problem occurs when using a local profile.
- When you set Local-Profiles-First=LPF-No, the MAX TNT waits for the remote authentication to time out before attempting to authenticate locally. This timeout might take longer than the timeout specified for the connection and could cause all connection attempts to fail. Therefore, set the authentication timeout value low enough to guard against the line going down, but high enough to permit the unit to respond if it can. The recommended time is 3 seconds.
Location: External-Auth
See Also: Auth-Timeout, Auth-Type
Location
Description: Specifies the physical location of the MAX TNT. An SNMP manager can both
read and set the Location value.
Usage: Specify text describing where the MAX TNT is located. You can enter up to 80
characters. The default is null.
Example: set location=building 64
Location: SNMP
See Also: Contact
Log
Description: A profile that specifies system-wide event-logging settings. System-wide event
logging includes the MAX TNT log buffer accessed by the Log command, and any Syslog host
designated by the Log profile. For information about the Log command, see Log.
Usage: Use the Read and List commands to make Log the working profile and list its
contents. For example:
admin> read log
LOG read
admin> list
save-level=info
save-number=100
call-info=none
syslog-enabled=no
host=0.0.0.0
port=514
facility=local0
syslog-format=tnt
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the profile. To close the profile and save your changes:
admin> write
LOG written
See Also: Facility, Host, Save-Level, Save-Number, Syslog-Enabled, Syslog-Format
Log-Display-Level
Description: Specifies the lowest level of the log messages that the MAX TNT displays to a
logged-in user.
Usage: Specify one of the following settings:
Example: set log-display-level=debug
Dependencies: Do not confuse Log-Display-Level with Save-Level in the Log profile.
Save-Level determines which messages are displayed in the event-log status window.
Location: User name
See Also: Log, Save-Level
Login-Prompt
Description: Specifies the string that acts as a prompt for a user name in the terminal-server
interface.
Description: If Prompt-Format=No, you can specify up to 15 characters, not including a
newline or tab character.
If Prompt-Format=Yes, you can specify up to 80 characters in multiple lines by including the newline (\n) and tab (\t) characters. To include an actual backslash character, you must precede it with another backslash. For example, suppose you enter the following string:
Welcome to\n\t\\Ascend Remote Server\\\nEnter your user name:
The terminal server displays the following text as the login prompt:
Welcome to
\Ascend Remote Server\
Enter your user name:
Regardless of the Prompt-Format setting, the default setting for Login-Prompt is Login:.
Example: set login-prompt=Login Name:
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled, Login-Prompt does not apply.
Location: Terminal-Server > Terminal-Mode-Configuration
See Also: Password-Prompt, Prompt, Prompt-Format, Terminal-Mode-Configuration,
Third-Login-Prompt, Third-Prompt-Sequence
Login-Timeout
Description: Specifies the number of seconds a user can wait to log into the terminal server.
When a user attempts to log into the terminal server in terminal mode, a login prompt appears.
If the user does not proceed any further than the login prompt within the number of seconds
you specify, the login times out.
Usage: Specify a number between 0 and 300. The default is 300. If you set Login-Timeout to
0 (zero), the login never times out.
Example: set terminal login-timeout=60
Location: Terminal-Server > Terminal-Mode-Configuration
See Also: Password-Prompt, Prompt, Prompt-Format, Terminal-Mode-Configuration,
Third-Login-Prompt, Third-Prompt-Sequence
Loop-Avoidance
Description: Specifies the number of transit devices through which the MAX TNT may route
a call.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 26. The default is 7.
Example: set loop-avoidance=7
Location: E1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface
See Also: Line-Interface, NL-Value
Loss-Of-Carrier
Description: Indicates a loss of the carrier signal on a T1 line.
Usage: The Loss-Of-Carrier setting is read only. True indicates a loss of carrier. False
indicates that the carrier is maintaining a connection.
Location: T1-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: AIS-Receive, BER-Receive, Carrier-Established, Loss-Of-Sync, Yellow-Receive
Loss-Of-Sync
Description: Indicates whether the T1 line has lost synchronization.
Usage: The Loss-Of-Sync setting is read only. True indicates that synchronization has been
lost. False indicates that synchronization is intact.
Location: T1-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: AIS-Receive, BER-Receive, Carrier-Established, Loss-Of-Carrier, Yellow-Receive
LQM
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT requests link-quality monitoring when
answering a PPP call. Link-quality monitoring counts the number of packets sent across the
link and periodically asks the remote end how many packets it has received. Discrepancies are
evidence of packet loss and indicate link-quality problems. Link-quality monitoring also
generates periodic link-quality reports, and the two ends of the link exchange the reports.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes specifies that the MAX TNT requests link-quality monitoring.
- No specifies that the MAX TNT does not request link-quality monitoring.
Example: set lqm=yes
Dependencies: The LQM value applies only to PPP links.
Location: Answer-Defaults > PPP-Answer, Connection station > PPP-Options
See Also: LQM-Maximum-Period, LQM-Minimum-Period, PPP-Answer, PPP-Options
LQM-Maximum-Period
Description: Specifies the maximum period, in one-hundredths of a second, during which the
MAX TNT will accept and send link-quality monitoring packets when answering a PPP call.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 600. The default is 600.
Example: set lqm-maximum-period=300
Dependencies: If LQM=No, LQM-Maximum-Period does not apply.
Location: Answer-Defaults > PPP-Answer, Connection station > PPP-Options
See Also: LQM, LQM-Minimum-Period, PPP-Answer, PPP-Options
LQM-Minimum-Period
Description: Specifies the minimum period, in one-hundredths of a second, during which the
MAX TNT will accept link-quality monitoring packets when answering a PPP call.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 600. The default is 600.
Example: set lqm-minimum-period=200
Dependencies: If LQM=No, LQM-Minimum-Period does not apply.
Location: Answer-Defaults > PPP-Answer, Connection station > PPP-Options
See Also: LQM, LQM-Maximum-Period, PPP-Answer, PPP-Options
M
MAC-Address
Description: Specifies the Media Access Control (MAC) address of an Ethernet interface. An
Ethernet MAC address is a 12-digit hexadecimal number denoting the physical address
encoded in the controller.
Usage: In most cases, the MAC-Address value is obtained from the system. However, you can
clone a profile by reading an existing one and changing its physical address.
Example: set mac-address=00:c0:6c:4e:ac:5a
Location: Ether-Info {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Interface-Address, Link-State
Maintenance-State
Description: Allows you to Busy Out or take Out Of Service (OOS) a T1 PRI line. Doing so
is known as quiescing the line to make it available for maintenance. Active calls on the line are
not torn down. When an active call disconnects, the MAX TNT takes the channel out of
service. When the entire line is out of service, it is available for maintenance.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes quiesces the line, making it available for maintenance when all active calls have been dropped.
- No specifies that the line is available for active service. If you specify No after the line has been quiesced, it returns to service.
Example: set maintenance-state=yes
Dependencies: If the line's Signaling-Mode is not ISDN, Maintenance-State does not apply.
When the MAX TNT reboots, all T1 PRI lines come up available for service.
Location: T1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface
See Also: Line-Interface, Signaling-Mode
Major-Firmware-Ver
Description: Indicates the major firmware version of the RADSL or SDSL card.
Usage: The Major-Firmware-Ver setting is read only.
Location: ADSL-Cap-Status {shelf-N slot-N N}, SDSL-Status {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Dev-Line-State, Down-Stream-Constellation, Down-Stream-Operational-Baud,
Down-Stream-Rate, Hardware-Ver, IF-Group-Index, Minor-Firmware-Ver, Physical-Address,
Unit-Type, Up-Stream-Constellation, Up-Stream-Rate
Mask
Description: Specifies a 12-byte mask to apply to a generic filter's Value setting before
comparing the Value to the packet contents at the specified Offset. You can use the mask to
specify exactly which bits you want to compare.
After translating Mask and Value into binary format, the MAX TNT applies the mask to the specified value by performing a logical AND. The mask hides the bits that appear behind each binary 0 (zero) in the mask. A mask of all ones (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) masks no bits, so the full specified value must match the packet contents.
Usage: Specify a hexadecimal number of up to 12 bytes. The default is 000000000000.
Example: offset=2
len=8
more=no
comp-neq=no
mask=0f:ff:ff:ff:00:00:00:f0:00:00:00:00
value=07:fe:45:70:00:00:00:90:00:00:00:00
Suppose you want to apply these Gen-Filter settings to the following packet contents:
2A 31 97 FE 45 70 12 22 33 99 B4 80 75
The MAX TNT applies the mask as shown below, resulting in a value that matches the Value setting.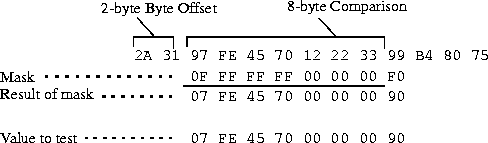
The packet matches the filter. Because Forward=No, the MAX TNT drops the packet. The byte comparison works as follows:
- The first two bytes, 2A and 31, are ignored because of the two-byte offset.
- The 9 in the third byte is ignored, because the mask has a 0 (zero) in its place. The 7 in the third byte matches the 7 in the Value setting for that byte.
- The F and E in the fourth byte match the Value setting for that byte.
- The 4 and 5 in the fifth byte match the Value setting for that byte.
- The 7 and 0 in the sixth byte match the Value setting for that byte.
- The 12, 22, and 33 in the seventh, eighth, and ninth bytes, respectively, are ignored because the mask has a 0 (zero) in those places.
- The first 9 in the tenth byte matches the Value setting of 9 in the first half of that byte. The second 9 in the packet's tenth byte is ignored because the mask has a 0 (zero) in its place.
Location: Filter filter-name > Input-Filters > Gen-Filter,
Filter filter-name > Output-Filters > Gen-Filter
See Also: Gen-Filter, Input-Filters, Output-Filters
Master-Shelf-Controller
Description: Specifies the number of the master shelf in a multishelf system.
Usage: Specify the number you set on the rotary switch. All shelves must agree upon the
master shelf.
Example: set master-shelf-controller=1
Dependencies: If Shelf-Controller-Type=Master, Master-Shelf-Controller does not apply.
You can set Master-Shelf-Controller for a slave shelf only.
Location: System
See Also: Shelf-Controller-Type
Max-Baud-Rate
Description: Specifies the highest baud rate that digital modems should attempt to negotiate.
Typically, the digital modems start with the highest possible baud rate (33600) and negotiate
down to the rate accepted by the remote modem. You can adjust the maximum rate to bypass
some of the negotiation cycles, provided that no incoming calls use a baud rate higher than the
value you specify for Max-Baud-Rate.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
33600-Max-Baud (the default)
31200-Max-Baud
28800-Max-Baud
26400-Max-Baud
2400-Max-Baud
21600-Max-Baud
19200-Max-Baud
16800-Max-Baud
14400-Max-Baud
12000-Max-Baud
9600-Max-Baud
7200-Max-Baud
4800-Max-Baud
2400-Max-Baud
Example: set max-baud-rate=31200-max-baud
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled, Max-Baud-Rate does not apply.
Location: Terminal-Server > Modem-Configuration
See Also: Down-Stream-Operational-Baud, Modem-Configuration
Max-Call-Duration
Description: Specifies the maximum number of minutes an incoming call can remain
connected. For a multichannel call, the maximum applies to each channel.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 1440. The MAX TNT checks the connection once per
minute, so the actual time the call is connected is slightly longer than the time you set. The
default is 0 (zero), which specifies that the MAX TNT does not set a limit on the duration of an
incoming call.
Location: Connection station > Session-Options
See Also: Session-Options
Max-Down-Stream-Rate
Description: Specifies the maximum down-stream rate supported by the ADSL-CAP card.
Specify one of the following settings to indicate the maximum down-stream rate the transceiver supports:
640000
960000
1280000
1600000
1920000
2240000
2560000
2688000
3200000
4480000
5120000
6272000
7160000
7168000
The CPE maximum down-stream rate defaults to 7,160,000. The COE maximum down-stream rate defaults to 2,560,000. To adjust the down-stream rates, configure the COE ADSL-CAP profile. The loop trains to the lower of the two rates.
If the loop quality is poor, the transceiver chooses a rate lower than the Maximum-Down-Stream-Rate setting. Good loop quality causes the transceiver to choose a rate close to or equal to the Maximum-Down-Stream-Rate setting. If the loop quality is very poor, the transceiver cannot train at all, and is unable to connect to the remote side. In the case of poor loop quality, you must specify a lower maximum down-stream rate, because the transceiver does not cross rate boundaries.
For example, if the transceiver is configured for 7,160,000 bps, and the loop quality is so poor that the transceiver cannot connect to the remote side, the transceiver does not automatically adjust the down-stream rate into the 5,120,000 bps range. You must configure the Max-Down-Stream-Rate to the lower rate.
Example: An administrator sets the maximum down-stream rate to 5.12Mbps:
admin> read adsl-cap {1 11 1}
ADSL-CAP/{ shelf-1 slot-11 1 } read
admin> set line-config max-down-stream-rate=5120000
admin> write
ADSL-CAP/{ shelf-1 slot-11 1 } written
The following example shows the status of the down-stream functionality as displayed in the ADSL-CAP-Status profile:
admin> read adsl-cap-status { 1 11 1}
ADSL-CAP-STATUS/{ shelf-1 slot-11 1 } read
admin> list
physical-address*={ shelf-1 slot-11 1 }
if-group-index=0
unit-type=coe
dev-line-state=port-up
up-stream-rate=952000
down-stream-rate=5120000
major-firmware-ver=232
minor-firmware-ver=0
hardware-ver=0
up-stream-constellation=256
down-stream-constellation=256u
down-stream-operational-baud=680
The Down-Stream-Operational-Baud setting now displays 680 and Down-Stream-Rate displays 5,120,000.
Dependencies: You can set the maximum down-stream rate for using SNMP utilities by writing
the DownRate object in the AdslCapLineStatusEntry MIB. The DownRate object supports
Read and Write operations. Valid values are 7168000, 5120000, and 2560000.
Location: ADSL-CAP {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Config
See Also: Down-Stream-Rate
Maximum-Channels
Description: Specifies the maximum number of channels in a multichannel call.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 32. The default is 2.
Example: set maximum-channels=5
Location: Answer-Defaults > MP-Answer, Connection station > MP-Options
See Also: Base-Channel-Count, Enabled, Minimum-Channels, MP-Answer, MP-Options
Maximum-Connect-Time
Description: Specifies the maximum number of minutes an AppleTalk Remote Access
(ARA) session can remain connected.
Usage: Specify an integer. The default is 0 (zero), which disables the timer. The maximum
connect time for an ARA connection has nothing to do with the MAX TNT idle timer. If you
specify a maximum connect time, the MAX TNT initiates an ARA disconnect when that time
is up. The ARA link goes down cleanly, but remote users are not notified. Users will find out
the ARA link is gone only when they try to access a device
Example: set maximum-connect-time=10
Dependencies: For Maximum-Connect-Time to apply, you must set Enabled=Yes in the
ARA-Answer subprofile and ARA-Enabled=Yes in the ARA-Options subprofile.
Location: Connection station > ARA-Options
See Also: ARA-Enabled
MAXLink-Client-Enabled
Description: Indicates whether the MAXLink client software is enabled.
Usage: The MAXLink-Client-Enabled setting is read only. Yes indicates that the MAXLink
client software is enabled. No indicates that the MAXLink client software is not enabled.
Example: maxlink-client-enabled=enabled
Location: Base
See Also: Frame-Relay-Enabled, Modem-Dialout-Enabled
Max-Tunnels
Description: Specifies the maximum number of mobile clients that can use Ascend Tunnel
Management Protocol (ATMP) to tunnel into the home network at the same time through the
connection.
Usage: Specify an integer. The default is 0 (zero). If you accept the default, the unit does not
enforce a limit.
Example: set max-tunnels=5
Dependencies: You must set Profile-Type=Gateway-Profile for the Max-Tunnels setting to
apply.
Location: Connection station > Tunnel-Options
See Also: Home-Agent-Password, Home-Network-Name, Primary-Home-Agent, Profile-Type
, Secondary-Home-Agent, UDP-Port
MBONE-LAN-Interface
Description: Specifies the interface address of the local Ethernet port on which the MBONE
router resides (the MBONE interface). The address can denote a local Ethernet port or a WAN
link, but not both.
Usage: Specify the MBONE interface address. The default is null.
Example: set mbone-lan-interface={ {shelf-1 slot-6 2} 0 }
Dependencies: Do not set both the MBONE-LAN-Interface and MBONE-Profile settings.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Interface-Address, MBONE-Profile, Multicast-Forwarding
MBONE-Profile
Description: Specifies the name of a Connection profile the MAX TNT uses to reach the
MBONE router.
Usage: Specify the name of a Connection profile. The default is null.
Example: set mbone-profile=mbone
Dependencies: Do not set both the MBONE-LAN-Interface and MBONE-Profile settings.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: MBONE-LAN-Interface, Multicast-Forwarding
Menu-Mode-Options
Description: A subprofile containing terminal-server configuration options for menu mode.
Usage: With Terminal-Server as the working profile, list the Menu-Mode-Options subprofile.
For example:
admin> list menu
start-with-menus=no
toggle-screen=no
remote-configuration=no
text-1=""
host-1=0.0.0.0
text-2=""
host-2=0.0.0.0
text-3=""
host-3=0.0.0.0
text-4=""
host-4=0.0.0.0
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Terminal-Server
See Also: Host-N (N=1-4), Remote-Configuration, Start-With-Menus, Text-N (N=1-4), Toggle-Screen
Metric
Description: Specifies a RIP-style metric for the route.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 15. The default is 1. The higher the metric, the less likely
that the MAX TNT uses the route.
Example: set metric=8
Location: IP-Route name
See Also: RIP, RIP-Mode, Routing-Metric
Minimum-Channels
Description: Specifies the minimum number of channels in a multichannel call.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 32. The default is 1.
Example: set minimum-channels=1
Location: Answer-Defaults > MP-Answer, Connection station > MP-Options
See Also: Base-Channel-Count, Enabled, Maximum-Channels, MP-Answer, MP-Options
Minor-Firmware-Ver
Description: Indicates the minor firmware version of the RADSL or SDSL card.
Usage: The Minor-Firmware-Ver setting is read only.
Location: ADSL-Cap-Status {shelf-N slot-N N}, SDSL-Status {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Dev-Line-State, Down-Stream-Constellation, Down-Stream-Operational-Baud,
Down-Stream-Rate, Hardware-Ver, IF-Group-Index, Major-Firmware-Ver, Physical-Address,
Unit-Type, Up-Stream-Constellation, Up-Stream-Rate
Modem-Configuration
Description: A subprofile containing options for configuring the unit's digital modems.
Usage: With Terminal-Server as the working profile, list the Modem-Configuration
subprofile. For example:
admin> list modem
v42/mnp=will-v42
max-baud-rate=33600-max-baud
modem-transmit-level=-10-db-mdm-trn-level
cell-mode-first=no
cell-level=-18-db-cell-level
7-even=no
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Terminal-Server
See Also: 7-Even, Cell-Level, Cell-Mode-First, Max-Baud-Rate, Modem-Transmit-Level,
V42/MNP
Modem-Dialout-Enabled
Description: Indicates whether modem dialout is enabled for the unit.
Usage: The Modem-Dialout-Enabled setting is read only. Yes indicates that modem dialout is
enabled. No indicates that modem dialout is disabled.
Example: modem-dialout-enabled=yes
Location: Base
See Also: Modem-Configuration, Modem-Disable-Mode, Modem-Table-Index,
Modem-Transmit-Level
Modem-Disable-Mode
Description: Specifies the state of each of the 48 modems in a card. The setting might also
affect a B channel of a T1 PRI line.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
Example: To disable modem 20 on shelf 1, slot 6:
admin> read lan {1 6 0}
LAN-MODEM/{ shelf-1 slot-6 0 } read
admin> list
physical-address*={ shelf-1 slot-6 0 }
modem-disable-mode=[enable enable enable enable enable enable enable +
admin> list modem-dis
...(All 48 modem settings are displayed)
admin> list 20
admin> set modem-dis=disable
Location: LAN-Modem {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Modem-Configuration, Modem-Dialout-Enabled, Modem-Table-Index,
Modem-Transmit-Level
Modem-Mod
Description: Sets the modem modulation to use when answering calls on a 56K modem.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
Example: set modem-mod=v34-modulation
Location: Terminal-Server > Modem Configuration
See Also: 7-Even, Cell-Level, Cell-Mode-First, Max-Baud-Rate, Modem-Transmit-Level,
V42/MNP
Modem-Table-Index
Description: Indicates the SNMP modem table index number of the device whose state is
described by the Admin-State profile.
Usage: The Modem-Table-Index setting is read only.
Location: Admin-State {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Modem-Configuration, Modem-Dialout-Enabled, Modem-Disable-Mode,
Modem-Transmit-Level
Modem-Transmit-Level
Description: Specifies the transmit attenuate level for a digital modem. When a modem calls
the MAX TNT, the unit attempts to connect at the transmit level you specify.
Usage: Generally, you do not need to change the transmit level. However, when the carrier is
aware of line problems or irregularities, you might need to alter the modem's transmit level by
specifying one of the following values:
-13-dB-Mdm-Trn-Level (-13 dB, the default)
-14-dB-Mdm-Trn-Level (-14 dB)
-15-dB-Mdm-Trn-Level (-15 dB)
-16-dB-Mdm-Trn-Level (-15 dB)
-17-dB-Mdm-Trn-Level (-15 dB)
-18-dB-Mdm-Trn-Level (-15 dB)
Example: set modem-transmit-level=-13-db-mdm-trn-level
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled, Modem-Transmit-Level does not apply. For
a 56K modem card, accept the default of -10-dB-Mdm-Trn-Level.
Location: Terminal-Server > Modem-Configuration
See Also: Modem-Configuration, Modem-Dialout-Enabled, Modem-Disable-Mode,
Modem-Table-Index
More
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT includes the next filter rule before determining
whether the frame matches the generic filter.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes links the current filter rule to the next one so that the filter can examine multiple noncontiguous bytes within a packet. The MAX TNT applies the next filter before deciding whether to forward the packet. The match occurs only if both sets of noncontiguous bytes contain the specified values.
- No does not link the current filter rule to the next one. The MAX TNT makes its forwarding decision solely on the basis of the current rule.
Example: set more=no
Dependencies: If you set More=Yes, the next filter must be enabled. Otherwise, the MAX
TNT ignores the filter.
Location: Filter filter-name > Input-Filters > Gen-Filter,
Filter filter-name > Output-Filters > Gen-Filter
See Also: Gen-Filter, Input-Filters, Output-Filters
MP-Answer
Description: An Answer-Defaults subprofile containing MP (RFC 1990) encapsulation
settings.
Usage: With Answer-Defaults as the working profile, list the MP-Answer subprofile. For
example:
admin> list mp-answer
enabled=yes
minimum-channels=1
maximum-channels=2
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Answer-Defaults
See Also: Enabled, Minimum-Channels, Maximum-Channels
MP-Options
Description: A Connection subprofile containing MP (RFC 1990) encapsulation settings.
Usage: With a Connection profile as the working profile, list the MP-Options subprofile. For
example:
admin> list mp-options
enabled=yes
base-channel-count=1
minimum-channels=1
maximum-channels=2
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Dependencies: MP encapsulation must be enabled in the Answer-Defaults profile.
Location: Connection station
See Also: Base-Channel-Count, Enabled, Minimum-Channels, Maximum-Channels
MPP-Answer
Description: An Answer-Defaults subprofile containing MP+ encapsulation settings.
Usage: With Answer-Defaults as the working profile, list the MPP-Answer subprofile. For
example:
admin> list mpp-answer
enabled=yes
dynamic-algorithm=quadratic
bandwidth-monitor-direction=transmit
increment-channel-count=1
decrement-channel-count=1
seconds-history=15
add-persistence=5
sub-persistence=10
target-utilization=70
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Answer-Defaults
See Also: Add-Persistence, Bandwidth-Monitor-Direction, Decrement-Channel-Count,
Dynamic-Algorithm, Enabled, Increment-Channel-Count, Seconds-History, Sub-Persistence,
Target-Utilization
MPP-Options
Description: A Connection subprofile containing MP+ encapsulation settings.
Usage: With a Connection profile as the working profile, list the MPP-Options subprofile. For
example:
admin> list mpp-options
enabled=yes
aux-send-password=""
dynamic-algorithm=quadratic
bandwidth-monitor-direction=transmit
increment-channel-count=1
decrement-channel-count=1
seconds-history=15
add-persistence=5
sub-persistence=10
target-utilization=70
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Dependencies: MP+ encapsulation must be enabled in the Answer-Defaults profile.
Location: Connection station
See Also: Add-Persistence, Aux-Send-Password, Bandwidth-Monitor-Direction, Decrement-Channel-Count
, Dynamic-Algorithm, Enabled, Increment-Channel-Count, Seconds-History
, Sub-Persistence, Target-Utilization
MRU
Description: Specifies the maximum number of bytes the MAX TNT can receive in a single
packet.
Usage: In most cases, you should accept the default setting for the connection. If you must
change the default, specify a value less than the default value.
- For a PPP connection, the default is 1524. Accept the default unless the device at the remote end of the link cannot support it.
- For a Frame Relay connection, the default is 1532.
Example: set mru=1524
Location: Answer-Defaults > PPP-Answer, Connection station > PPP-Options,
Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: PPP-Answer, PPP-Options
MTU-Limit
Description: Specifies a lower Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) value than the actual
path MTU of the link between a an Ascend Tunnel Management Protocol (ATMP) foreign
agent and home agent. The actual path MTU is determined by the type of connection.
Mobile clients use standard MTU discovery mechanisms to determine the path MTU, and then fragment packets at the appropriate size. However, to transmit packets through an ATMP tunnel, the MAX TNT adds an 8-byte GRE header and a 20-byte IP header to the frames it receives. This action can make the packet size larger than the MTU of the tunneled link, in which case the MAX TNT must either fragment the packet after encapsulating it, or reject the packet.
Usage: To avoid fragmenting packets after encapsulating them, set MTU-Limit to a value that
is 28 bytes less than the path MTU. If MTU-Limit is set to zero (the default), the MAX TNT
might have to fragment encapsulated packets before transmission. The other ATMP agent must
then reassemble the packets. If MTU-Limit is set to a nonzero value, the MAX TNT reports
that value to the client software as the path MTU, causing the client to send packets at the
specified size. Setting MTU-Limit to a nonzero value pushes the task of fragmentation and
reassembly out to the connection endpoints, lowering the overhead on the ATMP agents.
Example: set mtu-limit=1472
Location: ATMP
See Also: Agent-Mode, Agent-Type, Force-Fragmentation, Home-Agent-Password,
Retry-Limit, Retry-Timeout, UDP-Port
Multicast-Allowed
Description: Enables or disables multicasting on the IP interface.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes enables the MAX TNT to respond to IGMP client requests and responses.
- No specifies that the MAX TNT does not respond to multicast clients on the interface.
Example: set multicast-allowed=yes
Dependencies: If you set Multicast-Allowed=Yes and Multicast-Rate-Limit remains at the
default of 100, the MAX TNT handles IGMP responses and requests on the interface but does
not forward multicast traffic. You must set Multicast-Rate-Limit to a nondefault value before
the MAX TNT can forward multicast traffic.
Location: Connection station > IP-Options, IP-Interface {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: IP-Global, IP-Options, Multicast-Forwarding, Multicast-Member-Timeout, Multicast-Rate-Limit
Multicast-Forwarding
Description: Enables or disables multicast forwarding for the MAX TNT.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes enables multicast forwarding.
- No disables multicast forwarding.
Example: set multicast-forwarding=yes
Dependencies: Consider the following:
- For Multicast-Forwarding to have any effect, you must set MBONE-LAN-Interface or MBONE-Profile to specify the interface on which the MBONE router resides.
- When the value of Multicast-Forwarding changes from No to Yes, the multicast subsystem reads the values in the IP-Global profile and initiates the forwarding function. If you modify a multicast value in the IP-Global profile, you must set Multicast-Forwarding to No and then Yes again to force a read of the new values.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Allowed, Multicast-Member-Timeout, MBONE-LAN-Interface,
MBONE-Profile
Multicast-Group-Leave-Delay
Description: Specifies the number of seconds the MAX TNT waits before forwarding an
IGMP version 2 leave group message from a multicast client.
Usage: Specify a number of seconds from 0 to 120. The default is 0 (zero). If you specify a
value other than the default, and the MAX TNT receives a leave group message, the unit
sends an IGMP query to the WAN interface or client from which it received the leave
group message. If the MAX TNT does not receive a response from an active multicast client
that belongs to the client group, it sends a leave group message when the time you specify
expires.
If you accept the default, the MAX TNT forwards a leave group message immediately. If users might establish multiple multicast sessions for identical groups, set Multicast-Group-Leave-Delay to a value of 10 to 20 seconds.
Example: set multicast-group-leave-delay=15
Dependencies: Multicast-Group-Leave-Delay applies only if you set Multicast-Forwarding=Yes
and Multicast-Allowed=Yes.
Location: Connection > IP-Options, IP-Interface
See Also: Multicast-Allowed, Multicast-Forwarding, Multicast-Member-Timeout, Multicast-Rate-Limit
Multicast-Hbeat-Addr
Description: Specifies a multicast address for heartbeat monitoring. The MAX TNT listens
for packets to and from the associated group
When it runs as a multicast forwarder, the MAX TNT continually receives multicast traffic. Using heartbeat monitoring, you can monitor for possible connectivity problems by polling for multicast traffic. The MAX TNT generates an SNMP alarm trap if a traffic breakdown occurs.
Usage: Specify a multicast address in dotted decimal notation. The default is 0.0.0.0.
Example: set multicast-hbeat-addr=224.1.1.4
Dependencies: Consider the following:
- All the Multicast-Hbeat values interact to enable heartbeat monitoring. Heartbeat monitoring is an optional function. It is not required for multicast forwarding.
- Using the Multicast-Hbeat-Port, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr, and Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask settings, you can fine-tune the specification for which packets the MAX TNT monitors.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold, Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot, Multicast-Hbeat-Port
, Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask
Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold
Description: Specifies the minimum number of packets the MAX TNT can receive without
generating an alarm trap. If the number of monitored packets falls below the
Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold value, the MAX TNT sends the following SNMP alarm
trap:
Trap type: TRAP_ENTERPRISE
Code: TRAP_MULTICAST_TREE_BROKEN (19)
Arguments:
1) Multicast group address being monitored (4 bytes),
2) Source address of last heartbeat packet received (4 bytes)
3) Slot time interval configured in seconds (4 bytes),
4) Number of slots configured (4 bytes).
5) Total number of heartbeat packets received before the MAX TNT
started sending SNMP Alarms (4 bytes).
Usage: Specify an integer. The default is 0 (zero), which disables heartbeat monitoring.
Example: set multicast-hbeat-alarm-threshold=3
Dependencies: All the Multicast-Hbeat values interact to enable heartbeat monitoring. Heartbeat
monitoring is an optional function. It is not required for multicast forwarding.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Hbeat-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot, Multicast-Hbeat-Port, Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time
, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask
Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot
Description: Specifies how many times the MAX TNT polls before comparing the number of
multicast packets it received to the Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold value.
Usage: Specify the number of times the MAX TNT polls for packets. The default is 0 (zero).
Example: set multicast-hbeat-number-slot=5
In this example, if you set Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot to 5, and Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time to 3 seconds, the MAX TNT polls 5 times at 3-second intervals. After 60 seconds of elapsed time, it compares the number of multicast packets received to the alarm threshold.
Dependencies: All the Multicast-Hbeat values interact to enable heartbeat monitoring. Heartbeat
monitoring is an optional function. It is not required for multicast forwarding.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Hbeat-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold, Multicast-Hbeat-Port,
Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask
Multicast-Hbeat-Port
Description: Specifies a UDP port number. If specified, heartbeat monitoring listens only for
multicast packets received on that port.
Usage: Specify a UDP port number. The default is 0 (zero).
Example: set multicast-hbeat-port=16834
Dependencies: All the Multicast-Hbeat values interact to enable heartbeat monitoring. Heartbeat
monitoring is an optional function. It is not required for multicast forwarding.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Hbeat-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold, Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot
, Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask
Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time
Description: Specifies the interval (in seconds) in which the MAX TNT polls for multicast
traffic.
Usage: Specify the number of seconds between polling cycles. The default is 0 (zero).
Example: set multicast-hbeat-slot-time=6
Dependencies: All the Multicast-Hbeat values interact to enable heartbeat monitoring. Heartbeat
monitoring is an optional function. It is not required for multicast forwarding.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Hbeat-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold, Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot
, Multicast-Hbeat-Port, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask
Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr
Description: Specifies a multicast address. When it performs heartbeat monitoring, the MAX
TNT ignores packets from the IP address you specify.
Usage: Specify an IP address in dotted decimal notation. The default is 0.0.0.0.
Example: set multicast-hbeat-src-addr=10.1.2.3
Dependencies: All the Multicast-Hbeat values interact to enable heartbeat monitoring. Heartbeat
monitoring is an optional function. It is not required for multicast forwarding.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Hbeat-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold, Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot
, Multicast-Hbeat-Port, Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask
Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr-Mask
Description: Specifies a subnet mask that the MAX TNT applies to the
Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr value.
Usage: Specify a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation. The default is 0.0.0.0.
Example: set multicast-hbeat-src-addr-mask=255.255.255.0
Dependencies: All the Multicast-Hbeat values interact to enable heartbeat monitoring. Heartbeat
monitoring is an optional function. It is not required for multicast forwarding.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Hbeat-Addr, Multicast-Hbeat-Alarm-Threshold, Multicast-Hbeat-Number-Slot
, Multicast-Hbeat-Port, Multicast-Hbeat-Slot-Time, Multicast-Hbeat-Src-Addr
Multicast-Member-Timeout
Description: Specifies the timeout (in seconds) for client responses to multicast polling
messages.
When you configure the MAX TNT as a multicast forwarder, it forwards polling messages generated by the multicast router, and keeps track of active memberships from its client interfaces. If no client responds to the polling messages within the amount of time you specify for Multicast-Member-Timeout, the MAX TNT stops forwarding multicast traffic on that interface.
Usage: Specify an integer from 60 to 65535. The default is 360.
Example: set multicast-member-timeout=60
Dependencies: If Multicast-Forwarding=No, Multicast-Member-Timeout does not apply.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Multicast-Allowed, Multicast-Forwarding
Multicast-Rate-Limit
Description: Determines the rate at which the MAX TNT accepts multicast responses from
clients on the interface, and enables the MAX TNT to forward multicast traffic on the interface
(provided that Multicast-Allowed=Yes). The Multicast-Rate-Limit setting helps the forwarder
prevent multicast clients from creating response storms to multicast transmissions. It does not
affect the MBONE interface.
Usage: To begin forwarding multicast traffic on the interface, specify an integer lower than
100. The default is 100, which disables the forwarding of multicast traffic on the interface.
Example: set multicast-rate-limit=5
In this example, the MAX TNT accepts a packet from multicast clients on the interface every five seconds. The MAX TNT discards any subsequent packets received in that five-second window.
Dependencies: If you set Multicast-Allowed=Yes and Multicast-Rate-Limit remains at the
default of 100, the MAX TNT handles IGMP responses and requests on the interface but does
not forward multicast traffic. You must set Multicast-Rate-Limit to a nondefault value before
the MAX TNT can forward multicast traffic.
Location: Connection station > IP-Options, IP-Interface {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Multicast-Allowed
Multi-Rate-Enabled
Description: Indicates whether the unit can make DWS calls.
Usage: The Multi-Rate-Enabled setting is read only. Yes indicates that the unit can make
DWS calls. No indicates that the unit cannot make DWS calls.
Example: multi-rate-enabled=yes
Location: Base
See Also: R2-Signaling-Enabled, Switched-Enabled
Must-Accept-Address-Assign
Description: Instructs the MAX TNT to hang up if a caller rejects dynamic IP address
assignment.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes specifies that the caller must accept dynamic IP address assignment.
- No specifies that the MAX TNT allows the caller to reject the IP address offered by the MAX TNT and present its own IP address for consideration.
Example: set must-accept-address-assign=yes
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Assign-Address, Assign-Count, Pool-Base-Address, Pool-Summary
N
N391-Val
Description: Specifies the interval (in seconds) at which the MAX TNT requests a Full Status
Report about a Frame Relay link.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 255. The default is 6.
Example: set n391-val=15
Dependencies: If Link-Type=DCE, N391-Val does not apply.
Location: Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: Link-Type
N392-Val
Description: Specifies the number of errors, during DTE-N393-monitored events, that cause
the user side to declare the network side's procedures inactive.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 10. The value you enter should be less than N393-Val.
The default is 3.
Example: set n392-val=5
Dependencies: If Link-Type=DCE, N392-Val does not apply.
Location: Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: Link-Type, N393-Val
N393-Val
Description: Specifies the DTE-monitored event count.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 10. The value you enter should be greater than N392-Val.
The default is 4.
Example: set n393-val=6
Dependencies: If Link-Type=DCE, N393-Val does not apply.
Location: Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: Link-Type, N392-Val
Nailed-Group
Description: Assigns a group number to a T1 or E1 channel, to a nailed IDSL channel, or to a
SWAN line. You can then refer to the number in the Connection profile's Nailed-Groups
setting to specify the nailed-up channels a connection uses.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 65535. The default is 0 (zero).
Example: set nailed-group=7
Dependencies: Do not associate a group number with more than one active profile. For a T1
or E1 line, channels in a nailed-up group must be contiguous. For an IDSL card, only one
channel can be nailed up.
Location: E1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface > Channel-Config N,
IDSL {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface > Channel-Config N,
SWAN {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Config,
T1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface > Channel-Config N
See Also: Channel-Config N, Line-Config, Line-Interface, Nailed-Groups
Nailed-Groups
Description: Specifies one or more nailed-up groups belonging to a session.
Usage: Specify a number assigned to a group of nailed-up channels. For an MP+ connection,
you can assign more than one group number, separated by commas. The default is 1.
Example: set nailed-groups=1, 3
Dependencies: Only MP+ supports the use of multiple nailed-up groups.
Location: Connection station > Telco-Options
See Also: Call-Type, Nailed-Group, Telco-Options
Nailed-Mode
Description: Specifies how the MAX TNT uses the link's nailed-up channels, and whether
the link uses nailed-up channels alone, or a combination of nailed-up and switched channels.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- FT1 (the default) specifies that the link uses only nailed-up channels.
- FT1-MPP specifies that the link uses a combination of nailed-up and switched channels.
- FT1-BO specifies that the link uses a combination of nailed-up and switched channels with backup and overflow.
In providing backup bandwidth, the MAX TNT drops all the nailed-up channels when the quality of a nailed-up channel falls to Marginal or Poor in an FT1-BO call The MAX TNT then attempts to replace dropped nailed-up channels with switched channels. It also monitors dropped nailed-up channels. When the quality of all dropped channels changes to Fair or Good, the MAX TNT reinstates them.
In providing overflow protection, the MAX TNT supplies supplemental dial-up bandwidth during times of peak demand in order to prevent saturation of a nailed-up line. The circuit remains in place until the traffic subsides, and then it is removed.
Example: set nailed-mode=ft1
Location: Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: Nailed-Up-Group
Nailed-Up-Group
Description: Specifies the group number assigned to the nailed-up channels of a Frame Relay
link.
Usage: Specify a number assigned to a group of nailed-up channels. The maximum value you
can enter is 1024.
Example: set nailed-up-group=5
Location: Frame-Relay fr-name
See Also: Nailed-Mode
Name
Description: Assigns a name to a profile, user, route, host, or the MAX TNT system itself.
Usage: Specify a descriptive name. For all profiles except the IP-Route, IPX-Route, and Trap
profiles, you can specify up to 24 characters. For the IP-Route, IPX-Route, and Trap profiles,
you can specify up to 31 characters. The default is null in all except User profiles, where the
default is default.
Example: set name=newyork
Dependencies: If the MAX TNT uses the specified value for authentication, it is case sensitive.
In the SWAN profile, the Name setting identifies the line for administrative purposes
only. The unit uses only the Physical-Address setting to identify the SWAN line.
Location: ADSL-Cap {shelf-N slot-N N}, E1 {shelf-N slot-N N}, Firewall name,
IDSL {shelf-N slot-N N}, IP-Route name, IPX-Route name, SDSL {shelf-N slot-N N},
SWAN {shelf-N slot-N N}, System, T1 {shelf-N slot-N N}, T3 {shelf-N slot-N N},
Trap host-name, User name
See Also: ADSL-Cap, E1, Firewall, IP-Route, IPX-Route, Physical-Address, SDSL, SWAN,
System, T1, T3, Trap, User
Net-Alias
Description: Specifies the IPX network number of a remote router. The MAX TNT uses this
network number only when connecting to a non-Ascend router that uses numbered interfaces.
Usage: Specify the IPX network number of the remote device. The default of 00000000 is
appropriate for most installations. If you accept the default, the MAX TNT does not advertise
the route until it makes a connection to the remote network.
Dependencies: If the MAX TNT does not route IPX for the connection, or if IPX routing is
globally disabled, Net-Alias does not apply.
Location: Connection station > IPX-Options
See Also: Dial-Query, IPX-Header-Compression, IPX-Routing-Enabled,
IPX-SAP-HS-Proxy, IPX-SAP-HS-Proxy-Net, Net-Number, Peer-Mode, RIP, SAP, SAP-Filter
NetBIOS-Primary-NS
Description: Specifies the IP address of the primary NetBIOS server.
Usage: Specify the IP address in dotted decimal notation. The default is 0.0.0.0, which
indicates that no NetBIOS server exists.
Example: set netbios-primary-ns=10.1.2.3/24
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Domain-Name, NetBIOS-Secondary-NS
NetBIOS-Secondary-NS
Description: Specifies the IP address of the secondary NetBIOS server. The MAX TNT
accesses the secondary server if the primary NetBIOS server is unavailable.
Usage: Specify the IP address in dotted decimal notation. The default is 0.0.0.0, which
indicates that no secondary NetBIOS server exists.
Example: set netbios-secondary-ns=10.57.24.11/24
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Domain-Name, NetBIOS-Primary-NS
Net-Number
Description: Specifies the IPX network number of the remote router.
Usage: Specify the IPX network number of the remote device only when the router requires
that the MAX TNT know its network number before connecting. If you specify a value for
Net-Number, the MAX TNT creates a static route to the device. In addition, the MAX TNT
becomes a seed router, and other routers can learn the IPX network number from the MAX
TNT.
If there are other NetWare routers on the LAN interface, the IPX number assigned to the MAX TNT for that interface must be consistent with the number in use by the other routers. The best way to ensure consistency is to accept the default null address for Net-Number. The null address causes the MAX TNT to learn its network number from another router on the interface, or from the RIP packets received from the local IPX server.
The default of 00000000 is appropriate for most installations. If you accept the default, the MAX TNT does not advertise the route until it makes a connection to the remote network.
Dependencies: If the MAX TNT does not route IPX for the connection, or if IPX routing is
globally disabled, Net-Number does not apply.
Location: Connection station > IPX-Options
See Also: Dial-Query, IPX-Header-Compression, IPX-Routing-Enabled,
IPX-SAP-HS-Proxy, IPX-SAP-HS-Proxy-Net, Net-Alias, Peer-Mode, RIP, SAP, SAP-Filter
Network-Loopback
Description: Indicates whether the T1 line is looped back to the network.
Usage: The Network-Loopback setting is read only. True indicates that the T1 line is looped
back to the network. False indicates that the T1 line is not looped back to the network.
Location: T1-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: AIS-Receive, BER-Receive, Carrier-Established, Channel-State, Error-Count,
Line-State, Loss-Of-Carrier, Loss-Of-Sync, Physical-Address, Port-Enabled, Yellow-Receive
Network-Management-Enabled
Description: Indicates whether the network-management option is enabled.
Usage: The Network-Management-Enabled option is read only. Yes indicates that the
network-management option is enabled. No indicates that the network-management option is
disabled.
Example: network-management-enabled=yes
Location: Base
See Also: AIM-Enabled
New-NAS-Port-ID-Format
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT reports a value for the RADIUS NAS-Port
attribute appropriate to the multishelf and multislot architecture of the system.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is Yes.
- Yes specifies that the MAX TNT reports an NAS-Port value appropriate to the multishelf and multislot architecture. The value has the following format:
shelf slot line channel
where shelf indicates the shelf number (0-3), slot indicates the slot number (0-15), line indicates the line number (0-31), and channel indicates the channel number (0-31) for an ISDN call. For an analog call, the values are the same, except that the line number can be 0-63, and the channel number is always 1. When using the attribute for accounting purposes, you must add 1 to each component to ascertain the actual shelf, slot, line, and channel number.
No specifies that the MAX TNT reports an NAS-Port value in the following format:
tllcc
where t indicates 1 for a digital call or 2 for an analog call, ll indicates the line number, and cc indicates the channel number.
Example: set new-nas-port-id-format=no
Dependencies: If you set New-NAS-Port-ID-Format=No, the following conditions must be
met:
- Multishelf is not supported.
- All line cards must be placed contiguously in the first slots of the standalone system. Lines must be numbered 1 through 8 for slot 1, 9 through 16 for slot 2, and so on.
If RADIUS accounting or call logging is in use, do not change the New-NAS-Port-ID-Format setting while the system has active sessions.
Location: System
See Also: Analog-Encoding, Call-Routing-Sort-Method, Idle-Logout, Master-Shelf-Controller
, Name, Parallel-Dialing, SessionID-Base, Shelf-Controller-Type, Single-File-Incoming,
System-Rmt-Mgmt, Use-Trunk-Groups
NFAS-Group-ID
Description: Specifies the number of a Non-Facility Associated Signaling (NFAS) group.
Some sites require multiple NFAS groups on a single card to enable grouped DS1s. An NFAS group contains a minimum of two PRIs, so the T1 card supports up to four NFAS groups, and the T3 card supports up to 14 NFAS groups.
Usage: For a T1 card, set NFAS-Group-ID to a value from 0 to 3. For a T3 card, valid values
are from 0 to 13. Lines with the same NFAS-Group-ID value are in the same NFAS group.
Example: Two NFAS groups are configured on a T1 card, each containing four lines. This
example uses the NFAS group IDs 1 and 2, but you can assign any valid NFAS-Group-ID values.
The following commands configure NFAS group 1, which contains lines 1 through 4:
admin> read t1 {1 2 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=0
admin> set line nfas-group-id=1
admin> set channel 24 channel=nfas-primary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 2}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 2 } read
admin> set line sig=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=1
admin> set line nfas-group-id=1
admin> set line channel 24 channel=nfas-secondary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 2 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 3}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 3 } read
admin> set line sig=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=2
admin> set line nfas-group-id=1
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 3 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 4}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 4 } read
admin> set line sig=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=3
admin> set line nfas-group-id=1
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 4 } written
The following commands configure NFAS group 2, which contains lines 5 through 8:
admin> read t1 {1 2 5}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 5 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=0
admin> set line nfas-group-id=2
admin> set channel 24 channel=nfas-primary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 5 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 6}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 6 } read
admin> set line sig=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=1
admin> set line nfas-group-id=2
admin> set line channel 24 channel=nfas-secondary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 6 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 7}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 7 } read
admin> set line sig=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=2
admin> set line nfas-group-id=2
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 7 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 8}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 8 } read
admin> set line sig=isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id=3
admin> set line nfas-group-id=2
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 8 } written
Dependencies: To configure multiple NFAS groups, you must set both NFAS-Group-ID and
NFAS-ID for each DS1. Within the group, all PRIs share the same NFAS-Group-ID value and
have different, unique NFAS-ID values.
Location: T1 {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: NFAS-ID
NFAS-ID
Description: Specifies a group ID for T1 lines that use Non-Facility Associated Signaling
(NFAS). You must ask your service provider about the NFAS ID number to specify for each
line.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 31.
Example: set nfas-id=2
Dependencies: Consider the following:
- You assign a T1 line to an NFAS group by setting Signaling-Mode=ISDN-NFAS.
- Within the NFAS group, configure only a single line to provide the primary ISDN D channel, and another line to provide the secondary (backup) D channel.
Location: T1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface
See Also: Line-Interface, Signaling-Mode, Switch-Type
NL-Value
Description: Specifies the number of retransmissions the MAX TNT sends on the line.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 255. The default is 64. You must accept the default when
the line connects to a DPNSS or DASS2 switch.
Example: set nl-value=64
Location: E1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface
See Also: Line-Interface, Signaling-Mode, Switch-Type
Number-Complete
Description: Specifies the criteria for having received enough digits on an incoming call that
uses R2 signaling.
Usage: Specify 1-Digits, 2-Digits, and so on, up to 10-Digits, to specify up to ten
digits of a phone number. Or, to indicate that the full number has been received, accept the
default End-Of-Pulsing setting. For call-routing purposes, the digits received before the call is
answered are considered the called number.
Example: set number-complete=end-of-pulsing
Location: E1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface
See Also: Line-Interface, Signaling-Mode, Switch-Type
O
Offset
Description: Specifies a byte-offset from the start of a frame to the data the MAX TNT tests
against the generic filter. If the current filter is linked to the previous one (if More=Yes in the
previous filter), the offset starts at the endpoint of the previous segment.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 8. The default is 0 (zero), which indicates no offset.
Example: set offset=2
Location: Filter filter-name > Input-Filters > Gen-Filter,
Filter filter-name > Output-Filters > Gen-Filter
See Also: Gen-Filter, Input-Filters, Output-Filters
OSPF
Description: A subprofile that enables you to configure OSPF routing on an Ethernet
interface.
Note: For information about how to display statistical information related to OSPF routing,
see OSPF.
Usage: With IP-Interface as the working profile, list the OSPF subprofile. For example:
admin> list ospf
active=no
area=0.0.0.0
area-type=normal
hello-interval=10
dead-interval=40
priority=5
authen-type=simple
auth-key=ascend0
cost=1
ase-type=type-1
ase-tag=c0:00:00:00
transit-delay=1
retransmit-interval=5
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: IP-Interface {{shelf-N slot-N N} N}
See Also: Active, Area, Area-Type, ASE-Tag, ASE-Type, Authen-Type, Auth-Key, Cost,
Dead-Interval, Hello-Interval, Priority, Retransmit-Interval, Transit-Delay
OSPF-ASE-Pref
Description: Specifies the preference value for OSPF routes that the router learns about by
means of RIP, ICMP, or another non-OSPF protocol.
When choosing the routes to put in the routing table, the router first compares their preference values, preferring the lowest number. If the preference values are equal, the router compares the metric values, using the route with the lowest metric.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 255. A value of 255 prevents the use of the route.
Following are the default preferences for different types of routes:
- 0 (zero)-Connected routes
- 10-OSPF routes
- 30-Routes learned from ICMP redirects
- 100-Routes learned from RIP
- 100-Static routes
Example: set ospf-ase-pref=100
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Down-Preference, OSPF-Pref, Preference, RIP-Pref, Static-Pref
OSPF-Global
Description: A subprofile that enables you to define global OSPF behavior.
Usage: With IP-Global as the working profile, list the OSPF-Global subprofile. For example:
admin> list ospf-global
as-boundary-router=yes
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: IP-Global
See Also: AS-Boundary-Router
OSPF-Options
Description: A subprofile that contains settings for OSPF routing.
Usage: With a Connection profile as the working profile, list the OSPF-Options subprofile.
For example:
admin> list ip ospf
active=no
area=0.0.0.0
area-type=normal
hello-interval=30
dead-interval=120
priority=5
authen-type=simple
auth-key=ascend0
cost=10
ase-type=type-1
ase-tag=c0:00:00:00
transit-delay=1
retransmit-interval=5
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Connection station > IP-Options
See Also: Active, Area, Area-Type, ASE-Tag, ASE-Type, Authen-Type, Auth-Key, Cost,
Dead-Interval, Hello-Interval, Priority, Retransmit-Interval, Transit-Delay
OSPF-Pref
Description: Specifies the preference for routes that the router learns about by means of the
OSPF protocol.
When choosing the routes to put in the routing table, the router first compares their preference values, preferring the lowest number. If the preference values are equal, the router compares the metric values, using the route with the lowest metric.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 255. A value of 255 prevents the use of the route.
Following are the default preferences for different types of routes:
- 0 (zero)-Connected routes
- 10-OSPF routes
- 30-Routes learned from ICMP redirects
- 100-Routes learned from RIP
- 100-Static routes
- 100-ATMP routes
Example: set ospf-pref=10
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Down-Preference, OSPF-ASE-Pref, Preference, RIP-Pref, Static-Pref
Output-Filters
Description: A subprofile containing 12 output-filter configuration subprofiles. The MAX
TNT applies output filters to outgoing packets.
Usage: With a Filter profile as the working profile, use the List command to display the 12
subprofiles of the Output-Filters subprofile. For example:
admin> list output
output-filters[1]={ no no generic-filter { 0 0 no no 00:00:00:00:00:+
output-filters[2]={ no no generic-filter { 0 0 no no 00:00:00:00:00:+
output-filters[3]={ no no generic-filter { 0 0 no no 00:00:00:00:00:+
output-filters[4]={ no no generic-filter { 0 0 no no 00:00:00:00:00:+
...
To close the Output-Filters subprofile and return to a higher context in the profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Filter filter-name
See Also: Filter-Name, Input-Filters, Input-Filters N, Output-Filters N
Output-Filters N
Description: A subprofile containing one of the 12 levels of an output-filter specification in
an Output-Filters subprofile.
Usage: With a Filter profile as the working profile, list one of the 12 subprofiles. For example:
admin> list output 1
valid-entry=no
forward=no
type=generic-filter
gen-filter={ 0 0 no no 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 00:00:00:+
ip-filter={ 0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 none 0 none 0 no }
route-filter={ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 none }
ipx-filter={ 00:00:00:00 00:00:00:00 00:00:00:00:00:00 00:00:00:00:+
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Filter filter-name > Output-Filters
See Also: Filter-Name, Forward, Gen-Filter, Input-Filters, Input-Filters N, IP-Filter, Output-Filters
, Type, Valid-Entry
Output-IPX-SAP-Filters
Description: A subprofile that defines up to eight output filters for SAP packets. The MAX
TNT applies output filters to SAP response packets it transmits. If it receives a SAP request
packet, the MAX TNT applies output filters before transmitting the SAP response, and
excludes services from (or includes them in) the response packet as specified by the filter
conditions.
Usage: With IPX-SAP-Filter as the working profile, use the List command to display one of
the Output-IPX-SAP-Filters subprofiles. For example:
admin> list output 1
valid-filter=no
type-filter=exclude
server-type=00:00
server-name=""
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: IPX-SAP-Filter
See Also: Server-Name, Server-Type, Type-Filter, Valid-Filter
P
Parallel-Dialing
Description: Specifies the total number of calls that the MAX TNT can place at the same
time.
Usage: Specify an integer from 1 to 65535. If the MAX TNT has trouble establishing an
initial connection at the full bandwidth for calls from the U.S. to another country, reduce
Parallel-Dialing to a value of 1. For ADSL or SDSL operation, you must set Parallel-Dialing to
the number of ADSL or SDSL interfaces. The default is 2.
Example: set parallel-dialing=12
Location: System
See Also: Dial-Number
Password
Description: Specifies a password that the user must enter in order to log in.
Usage: Specify a text string of up to 20 characters. The default is null. The value you enter is
case sensitive.
Example: set password=Ascend
Location: User name
See Also: Aux-Send-Password, Recv-Password, Security-Mode, Send-Password, System-Password
, Telnet-Password
Password-For-Direct-Access
Description: Specifies the password the user must enter when
Security-For-Direct-Access=Global.
Usage: Specify a password of up to 64 characters. The default is null.
Example: set password-for-direct-access=mypassword
Dependencies: Consider the following:
- If Security-For-Direct-Access is not set to Global, the Password-For-Direct-Access setting is ignored.
- If Direct-Access=No, Password-For-Direct-Access does not apply.
Location: Terminal-Server > Dialout-Configuration
See Also: Direct-Access, Port-For-Direct-Access, Security-For-Direct-Access
Password-Prompt
Description: Specifies the string the terminal server uses to prompt for the System-Password
when authentication is in use and an interactive user initiates a connection.
Usage: Specify up to 15 characters. The default is Password:
Example: set password-prompt=Your Password:
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled, Password-Prompt does not apply.
Location: Terminal-Server > Terminal-Mode-Configuration
See Also: Login-Prompt, Prompt, Prompt-Format, Terminal-Mode-Configuration,
Third-Login-Prompt, Third-Prompt-Sequence
Peer-Mode
Description: Specifies whether the remote IPX caller is an IPX router or a dial-in client.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- Router-Peer (the default) specifies that the caller is an IPX router.
- Dialin-Peer specifies a dial-in client.
Dependencies: Consider the following:
- If you specify Dialin-Peer, the MAX TNT negotiates a routing session with the client by assigning the client a node address on the virtual IPX network defined by
IPX-Dialin-Pool. The client must accept the network number that the MAX TNT assigns. If the client has its own node number, the MAX TNT uses that number to form the full network address. If the client does not have a node number, the MAX TNT assigns it a unique node address on the virtual network.
- For dial-in clients, the MAX TNT does not send RIP and SAP advertisements across the connection, and it ignores RIP and SAP advertisements received from the remote end. However, it does respond to RIP and SAP queries it receives from dial-in clients.
- If the MAX TNT does not route IPX for the connection, or if IPX routing is globally disabled, Peer-Mode does not apply.
Location: Connection station > IPX-Options
See Also: Atalk-Peer-Mode, Dial-Query, IPX-Dialin-Pool, IPX-Header-Compression,
IPX-Routing-Enabled, IPX-SAP-HS-Proxy, IPX-SAP-HS-Proxy-Net, Net-Alias, Net-Number
, Peer-Mode, RIP, SAP, SAP-Filter
Perm-Conn-Upd-Mode
Description: Specifies under what circumstances the MAX TNT performs nonintrusive
remote updates of the configurations of permanent connections.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- All (the default) specifies that, if they are fetched from the RADIUS server, all existing permanent connections will be torn down and reestablished.
- Changed specifies that only changed permanent connections will be torn down and reestablished.
Example: set perm-conn-upd-mode=changed
Location: System
See Also: Analog-Encoding, Call-Routing-Sort-Method, Idle-Logout, Master-Shelf-Controller
, Name, New-NAS-Port-ID-Format, Parallel-Dialing, SessionID-Base, Shelf-Controller-Type
, Single-File-Incoming, System-Rmt-Mgmt, Use-Trunk-Groups
Phone-Number
Description: Specifies a phone number.
- In a Call-Route profile, the Phone-Number setting indicates "route any calls received on this number to me (the index address)."
- In a Frame-Relay profile, the Phone-Number setting indicates the number the MAX TNT dials to reach the switch.
- In a T1 or E1 profile, the Phone-Number setting assigns a channel an add-on number for outgoing calls.
Usage: Specify a phone number of up to 24 characters, limited to the following:
1234567890()[]!z-*|
The default is null.
Example: set phone-number=1212
Dependencies: If a nailed-up Frame-Relay datalink connection is in use, Phone-Number does
not apply.
Location: Call-Route {{{shelf-N slot-N N} N} N},
E1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface > Channel-Config N, Frame-Relay fr-name,
T1 {shelf-N slot-N N} > Line-Interface > Channel-Config N
See Also: Call-Route-Type, Channel-Config N, Index, Line-Interface, Preferred-Source,
Trunk-Group
PHS-Support
Description: Indicates whether support for the Personal Handyphone System (PHS) is
enabled.
Usage: The PHS-Support setting is read only. Yes indicates that PHS support is enabled. No
indicates that PHS support is disabled.
Example: phs-support=yes
Location: Base
See Also: Countries-Enabled, MAXLink-Client-Enabled, Multi-Rate-Enabled, R2-Signaling-Enabled
, Selectools-Enabled
Physical-Address
Description: Identifies a physical address.
Usage: The physical address has the format {shelf slot item}, where:
Syntax element
|
Description
|
|---|
shelf
|
Specifies the shelf in which the item resides. If you are using a
single-shelf system, the shelf number is always 1. For call-routing
purposes, a value of 0 (zero) or any-shelf specifies any shelf.
|
slot
|
Specifies the number of the item's expansion slot. Physical expansion slots are numbered from 1 to 16, starting with 1 for the slot just below the shelf controller. The slot value 17, controller, or c specifies the shelf controller card. For call-routing purposes, a value of 0 (zero) or any-slot specifies any slot.
For example, to address the first slot on shelf 1:
{ 1 1 0 }
|
item
|
Specifies an item, such as a digital modem or T1 line, on the slot card. Items are numbered starting with #1 for the leftmost item on the card. An item number of 0 (zero) denotes the entire slot.
For example, to address modem #48 on a modem card in slot #2 on shelf 1:
{ 1 2 48 }
|
In most cases, the value of Physical-Address is obtained from the system. However, you can clone a profile by reading an existing one and changing its physical address. Use the List and Set commands to modify the Physical-Address value. For example:
admin> list physical
shelf=shelf-1
slot=slot-9
item-number=37
admin> set shelf=shelf-2
As an alternative, you can just use the Set command. For example:
admin> set physical shelf=shelf-2
Location: ADSL-Cap {shelf-N slot-N N},
ADSL-Cap-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N},
ADSL-Cap-Statistics {shelf-N slot-N N},
ADSL-Cap-Status {shelf-N slot-N N},
E1 {shelf-N slot-N N},
IDSL {shelf-N slot-N N},
IDSL-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N},
LAN-Modem {shelf-N slot-N N},
SDSL {shelf-N slot-N N},
SDSL-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N},
SDSL-Statistics {shelf-N slot-N N},
SDSL-Status {shelf-N slot-N N},
Serial {shelf-N slot-N N},
SWAN {shelf-N slot-N N},
SWAN-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N},
T1 {shelf-N slot-N N},
T1-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N},
T3 {shelf-N slot-N N},
T3-Stat {shelf-N slot-N N}
See Also: Device-Address, Interface-Address, Item-Number, Shelf, Slot
Ping
Description: Enables and disables the terminal-server Ping command.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes enables terminal-server users to use the Ping command.
- No disables the Ping command in the terminal-server interface.
Example: set ping=yes
Location: Terminal-Server > Terminal-Mode-Configuration
See Also: PPP, Rlogin, SLIP, TCP, Telnet, Terminal-Mode-Configuration, Traceroute
Pool-Base-Address
Description: Specifies the base addresses of up to 128 IP address pools. A contiguous block
of addresses must be available, starting with the address you specify.
Usage: For each pool, specify the base IP address of a block of contiguous addresses. The
default is 0.0.0.0.
Example: set pool-base-address 3=10.207.23.1
Dependencies: Consider the following:
- An address in a pool does not accept a subnet mask modifier, because pool addresses are advertised as host routes. If you allocate IP addresses on a separate IP network or subnet, make sure you inform other IP routers about the route to that network or subnet.
- The number of addresses in the pool must be specified by Assign-Count.
- If you are using network summarization (by means of the Pool-Summary setting), the address you specify must be network aligned.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Assign-Address, Assign-Count, Must-Accept-Address-Assign, Pool-Name,
Pool-Summary
Pool-Name
Description: Assigns a name to an IP address pool for TACACS+ authentication. Each pool
configuration consists of a base address (specified by Pool-Base-Address), address count
(specified by Assign-Count), and name (specified by Pool-Name).
Usage: Specify a name of up to 11 characters. The default is null.
Example: set pool-name 1=newyork
Dependencies: If TACACS+ authentication is not in use, the MAX TNT treats a pool name
specification as a comment.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Assign-Address, Assign-Count, Must-Accept-Address-Assign, Pool-Base-Address,
Pool-Summary
Pool-OSPF-Adv-Type
Description: Specifies how to import summarized pool addresses into OSPF.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- Type-1 (the default) instructs the MAX TNT to import the pool addresses into OSPF as external Type-1 routes.
- Type-2 instructs the MAX TNT to import the pool addresses into OSPF as external Type-2 routes.
- Internal instructs the MAX TNT to import the pool addresses into OSPF as Intra-Area routes.
Example: set pool-ospf-adv-type=type-2
Dependencies: For Pool-OSPF-Adv-Type to apply, you must set Pool-Summary=Yes and
enable OSPF. For a change in the Pool-OSPF-Adv-Type setting to take effect, you must reset
the MAX TNT.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Active, Pool-Summary
Pool-Summary
Description: Specifies whether pool summarization is in use.
When Pool-Summary=Yes, the MAX TNT adds IP addresses from an address pool to the routing table as individual host routes, and summarizes the series of host routes into a network route advertisement. It advertises the entire pool as a route, and only privately knows which IP addresses in the pool are active. If a remote network sends a packet to an inactive IP address, the MAX TNT either bounces the packet back to the remote network or silently discards it.
When you use pool summarization, you significantly reduce the size of routing table advertisements.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes enables pool summarization.
- No disables pool summarization.
Example: set pool-summary=yes
Dependencies: If you set Pool-Summary=Yes, you must create a network-aligned pool that
adheres to the following rules:
- The value of Assign-Count must be two less than the total number of addresses in the pool. Add two to Assign-Count for the total number of addresses in the subnet, and calculate the subnet mask for the subnet on the basis of the total.
- Pool-Base-Address must be the first host address. Subtract 1 from the Pool-Base-Address to obtain the base address for the subnet.
For example, the following configuration creates a network-aligned address pool and enables pool summarization:
admin> set pool-base-address=10.12.253.1
admin> set assign-count=62
admin> set pool-summary=yes
Note the following:
- When you subtract one from the value of Pool-Base-Address in this example, you get 10.12.253.0, which is a valid base address for the 255.255.255.192 subnet mask. (Note that 10.12.253.64, 10.12.253.128, and 10.12.253.192 are also valid zero addresses for the same subnet mask.) The resulting address pool network is 10.12.253.0/26.
- When you add 2 to Assign-Count, you get 64. The subnet mask for 64 addresses is 255.255.255.192 (256-64=192). The Ascend notation for a 255.255.255.192 subnet mask is /26.
After verifying that every one of the configured address pools is network aligned, you must enter a static route for them. The static route handles all inactive IP address by routing them to the reject interface or the blackhole interface.
Location: IP-Global
See Also: Assign-Count, Pool-Base-Address, Pool-Name
Port
Description: Specifies the port number, as follows:
- In a Connection profile, the Port setting specifies the port on the login host to which TCP-Clear sessions connect.
- In the Terminal-Server profile, the Port setting specifies the port on the login host to which the user connects in immediate mode.
- In a Log profile, the Port setting specifies the destination port of the Syslog host.
Usage: Specify a port number. For a Connection or Terminal-Server profile, the default is 0
(zero). For the Log profile, the default is 514.
Example: set port=23
Dependencies: In the Log profile, Port does not apply if Syslog is disabled.
Location: Connection station > TCP-Clear-Options, Log,
Terminal-Server > Immediate-Mode-Options
See Also: Facility, Host, Immediate-Mode-Options, Save-Level, Save-Number, Service, Syslog-Enabled
, TCP-Clear-Options
Port-Enabled
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT sends trap-PDUs to the SNMP manager.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes specifies that theMAX TNT sends trap-PDUs to the host specified by Host-Address.
- No specifies that the MAX TNT does not send trap-PDUs.
Example: set port-enabled=yes
Location: Trap host-name
See Also: Alarm-Enabled, Community-Name, Host-Address, Host-Name, Security-Mode
Port-For-Direct-Access
Description: Specifies a Telnet port number to use for direct-access dialout service.
To dial out, a local operator uses Telnet to connect to the specified port. When the connection to the modem is established, the user can issue AT commands to the modem as if connected locally to its asynchronous port.
Usage: Specify a port number from 5000 to 32767. The default is 5000.
Example: set port-for-direct-access=23
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled or Direct-Access=No,
Port-For-Direct-Access does not apply.
Location: Terminal-Server > Dialout-Configuration
See Also: Dialout-Allowed, Dialout-Configuration, Direct-Access, Password-For-Direct-Access
, Port-For-Direct-Access, Security-For-Direct-Access, Telnet
PPP
Description: Enables or disables the use of the PPP command in the terminal-server interface.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes enables the use of the PPP command in the terminal-server interface.
- No disables the use of the PPP command in the terminal-server interface.
Example: set ppp=yes
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled, PPP does not apply.
Location: Terminal-Server > PPP-Mode-Configuration
See Also: Ping, PPP-Mode-Configuration, Rlogin, SLIP, TCP, Telnet, Terminal-Mode-Configuration
, Traceroute
PPP-Answer
Description: A subprofile containing default settings for PPP calls. The MAX TNT also uses
the PPP-Answer settings for the PPP variants, MP and MP+.
Usage: With Answer-Defaults as the working profile, list the PPP-Answer subprofile. For
example:
admin> list ppp-answer
enabled=yes
receive-auth-mode=no-ppp-auth
disconnect-on-auth-timeout=yes
link-compression=none
mru=1524
lqm=no
lqm-minimum-period=600
lqm-maximum-period=600
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Answer-Defaults
See Also: Disconnect-On-Auth-Timeout, Enabled, Link-Compression, LQM, LQM-Maximum-Period
, LQM-Minimum-Period, MRU, Receive-Auth-Mode
PPP-Mode-Configuration
Description: A subprofile containing terminal-server options for PPP sessions.
Usage: With Terminal-Server as the working profile, list the PPP-Mode-Configuration
subprofile. For example:
admin> list ppp-mode-configuration
ppp=yes
delay=5
direct=no
info=session-ppp
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: Terminal-Server
See Also: Delay, Direct, Info, PPP
PPP-Options
Description: A subprofile that contains settings for PPP calls. The MAX TNT also uses the
PPP-Options settings for the PPP variants, MP and MP+.
Usage: With a Connection profile as the working profile, list the PPP-Options subprofile. For
example:
admin> list ppp-options
send-password=""
recv-password=""
enabled=yes
link-compression=stac
mru=1524
lqm=no
disconnect-on-auth-timeout=yes
lqm-minimum-period=600
lqm-maximum-period=600
split-code-dot-user-enabled=no
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Dependencies: PPP calls must be enabled in the Answer-Defaults profile.
Location: Connection station
See Also: Disconnect-On-Auth-Timeout, Enabled, Link-Compression, LQM, LQM-Maximum-Period
, LQM-Minimum-Period, MRU, Recv-Password, Send-Password,
Split-Code-Dot-User-Enabled
Preference
Description: Specifies the preference for the route.
When choosing the routes to put in the routing table, the router first compares their preference values, preferring the lowest number. If the preference values are equal, the router compares the metric values, using the route with the lowest metric.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 255. A value of 255 prevents the use of the route, and is
valid only for a WAN route specified by a Connection profile. Following are the default
preferences for different types of routes:
- 0 (zero)-Connected routes
- 10-OSPF routes
- 30-Routes learned from ICMP redirects
- 100-Routes learned from RIP
- 100-Static routes
- 100-ATMP routes
Example: set preference=100
Location: Connection station > IP-Options, IP-Route name
See Also: Down-Preference, IP-Options, OSPF-ASE-Pref, OSPF-Pref, RIP-Pref, Static-Pref
Preferred-Source
Description: Specifies the address of a network port used as a T1 or E1 channel. The
Preferred-Source setting indicates "route calls received on this channel to me (the index
address)."
Usage: Specify the address of a T1 or E1 channel. The default is null.
Example: set preferred-source={{1 7 7} 0}
Location: Call-Route {{{shelf-N slot-N N} N} N}
See Also: Call-Route-Type, Index, Phone-Number, Trunk-Group
Primary-Home-Agent
Description: Specifies the IP address or hostname of the Ascend Tunnel Management
Protocol (ATMP) primary home agent.
Usage: Specify an IP address in dotted decimal notation, or a symbolic hostname containing
up to 31 characters. The default is 0.0.0.0.
If you specify a hostname, the MAX TNT uses the Domain Name System (DNS) to look up the host IP address. If the home agent requires a UDP port number different from the value specified by UDP-Port, you can specify a port value by appending a colon character (:) and the port number to the IP address or hostname. For example:
admin> set primary-home-agent=10.11.22.33:8877
admin> set primary-home-agent=home-agent.company.com:6969
The home agent IP address should be the system address, not the IP address of the interface on which the home agent receives tunneled data.
Dependencies: You must set Profile-Type=Mobile Client for the Primary-Home-Agent setting
to apply.
Location: Connection station > Tunnel-Options
See Also: Home-Agent-Password, Home-Network-Name, Max-Tunnels, Profile-Type, Secondary-Home-Agent
, UDP-Port
Priority
Description: Specifies the priority of the OSPF router with regard to designated-router (DR)
and backup designated-router (BDR) election. The MAX TNT can function as either a DR or a
BDR. However, many sites choose to assign these functions to LAN-based routers in order to
dedicate the MAX TNT to WAN processing.
Usage: Specify an integer. The default is 5.
Choose the DR- and BDR- election priority on the basis of each device's processing power and reliability. Assigning a priority of 1 or greater places the MAX TNT on the list of possible DRs and BDRs. A priority value of 0 (zero) excludes the MAX TNT from becoming a DR or BDR. The higher the priority value of the MAX TNT relative to other OSPF routers on the network, the better the chances that it will become a DR or BDR.
Example: set priority=10
Location: IP-Interface {{shelf-N slot-N N} N} > OSPF,
Connection station > IP-Options > OSPF-Options
See Also: IP-Options, OSPF, OSPF-Options
Private-Route
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT advertises route information by means of
routing protocols.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes makes the route private. The MAX TNT uses the route internally, but does not advertise it.
- No specifies that the MAX TNT advertises the route by means of routing protocols.
Example: set private-route=yes
Location: IP-Route name, Connection station > IP-Options
See Also: IP-Options, IP-Routing-Enabled, OSPF, RIP, RIP-Mode
Profile-Name
Description: Specifies the name of the Connection profile the MAX TNT uses to reach the
IPX network. When the MAX TNT receives a query for the specified server or a packet
addressed to that server, it finds the Connection profile and dials the connection.
Usage: Specify a text string representing the name of the Connection profile. You can enter up
to 24 characters. The default is null.
Example: set profile-name=tim
Location: IPX-Route name
See Also: Active-Route, Dest-Network, Host, Name, Server-Node, Server-Socket,
Server-Type, Ticks
Profiles-Required
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT rejects incoming calls for which it could find
neither a Connection profile nor an entry on a remote authentication server. If you do not
require a configured profile for all callers, the MAX TNT builds a temporary profile for
unknown callers. Many sites consider the use of a temporary profile a security breach, and
require that all callers have a configured profile.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is Yes.
- Yes specifies that the MAX TNT requires a configured profile for all callers. The unit rejects calls for which it cannot find a configured profile.
- No specifies that if the MAX TNT cannot find a configured profile, it creates a temporary profile for the caller.
Example: set profiles-required=no
Dependencies: You cannot set Profiles-Required for terminal-server calls.
Location: Answer-Defaults
See Also: Local-Profiles-First, Receive-Auth-Mode
Profile-Type
Description: Specifies the type of Ascend Tunnel Management Protocol (ATMP) connection.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- Disabled (the default) specifies that the connection is not used for ATMP.
- Mobile-Client specifies that the Connection profile is used to authenticate a mobile client.
- Gateway-Profile specifies that the Connection profile sets up a gateway-mode connection to a home network.
Example: set profile-type=gateway-profile
Location: Connection station > Tunnel-Options
See Also: Home-Agent-Password, Home-Network-Name, Max-Tunnels, Primary-Home-Agent
, Secondary-Home-Agent, UDP-Port
Prompt
Description: Specifies a string that the MAX TNT uses as a command-line prompt.
Usage: Specify a string to be used as a prompt. You can specify up to 15 characters. The
defaults are as follows:
- In a User profile, the default is an asterisk, which causes the MAX TNT to substitute the value of the profile's name upon successful login. For example, for the
admin profile, the prompt is admin>.
- In a Terminal-Server profile, the default is
ascend%
Example: set prompt=virginia>
Location: Terminal-Server > Terminal-Mode-Configuration, User name
See Also: Login-Prompt, Password-Prompt, Prompt-Format, Terminal-Mode-Configuration,
Third-Login-Prompt, Third-Prompt-Sequence
Prompt-Format
Description: Specifies whether the MAX TNT interprets carriage-return/linefeed and tab
characters in the string specified by Login-Prompt.
Usage: Specify Yes or No. The default is No.
- Yes causes the MAX TNT to interpret carriage-return/linefeed and tab characters in the string specified by Login-Prompt.
- No causes the MAX TNT to ignore carriage-return/linefeed or tab characters in the string specified by Login-Prompt.
Example: set prompt-format=no
Dependencies: If terminal services are disabled, Prompt-Format does not apply.
Location: Terminal-Server > Terminal-Mode-Configuration
See Also: Login-Prompt, Password-Prompt, Prompt, Terminal-Mode-Configuration,
Third-Login-Prompt, Third-Prompt-Sequence
Protocol
Description: Specifies a protocol type by number. The MAX TNT compares the number you
specify to the protocol number field in an IP packet. The default protocol number of 0 (zero)
matches all protocols.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
0-Disregard protocol type when applying the filter
1-ICMP (Internet Control Message protocol)
2-IGMP (Internet Group Management protocol)
3-GGP (Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol)
4-IP (Internet Protocol)
5-ST (Stream)
6-TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
7-UCL
8-EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol)
9-Any private interior gateway protocol
10-BBN-RCC-MON (BBN RCC Monitoring)
11-NVP-II (Network Voice Protocol II)
12-PUP
13-ARGUS
14-EMCOM
15-XNET (Cross-Net Debugger)
16-CHAOS
17-UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
18-MUX (Multiplexing)
19-DCN-MEAS (DCN Measurement Subsystems)
20-HMP (Host Monitoring Protocol)
21-PRM (Packet Radio Measurement)
22-XNS IDP (Xerox Networking System Internetwork Datagram Protocol)
23-TRUNK-1
24-TRUNK-2
25-LEAF-1
26-LEAF-2
27-RDP (Reliable Data Protocol)
28-IRTP (Internet Reliable Transport Protocol)
29-ISO-TP4 (International Standards Organization Transport Protocol Class 4)
30-NETBLT (Bulk Data Transfer Protocol)
31-MFE-NSP (MFE Network Services Protocol)
32-MERIT-INP (MERIT Internodal Protocol)
33-SEP (Sequential Exchange Protocol)
34-3PC (Third Party Connect Protocol)
35-IDPR (Inter-Domain Policy Routing Protocol)
36-XTP
37-DDP (Datagram Delivery Protocol)
38-IDPR-CMTP (IDPR Control Message Transport Protocol)
39-TP++ (TP++ Transport Protocol)
40-IL (IL Transport Protocol)
41-SIP (Simple Internet Protocol)
42-SDRP (Source Demand Routing Protocol)
43-SIP-SR (SIP Source Route)
44-SIP-FRAG (SIP Fragment)
45-IDRP (Inter-Domain Routing Protocol)
46-RSVP (Reservation Protocol)
47-GRE (General Routing Encapsulation)
48-MHRP (Mobile Host Routing Protocol)
49-BNA
50-SIPP-ESP (SIPP Encap Security Payload)
51-SIPP-AH (SIPP Authentication Header)
52-I-NLSP (Integrated Net Layer Security Protocol)
53-SWIPE (IP with Encryption)
54-NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol)
55-60-Unassigned
61-Any Host Internet Protocol
62-CFTP
63-Any local network
64-SAT-EXPAK (SATNET and Backroom EXPAK)
65-KRYPTOLAN
66-RVD (MIT Remote Virtual Disk Protocol)
67-IPPC (Internet Pluribus Packet Core)
68-Any distributed file system
69-SAT-MON (SATNET Monitoring)
70-VISA (VISA Protocol)
71-IPCU (Internet Packet Core Utility)
72-CPNX (Computer Protocol Network Executive)
73-CPHB (Computer Protocol Heart Beat)
74-WSN (Wang Span Network)
75-PVP (Packet Video Protocol)
76-BR-SAT-MON (Backroom SATNET Monitoring)
77-SUN-ND PROTOCOL-Temporary
78-WB-MON (WIDEBAND Monitoring)
79-WB-EXPAK (WIDEBAND EXPAK)
80-ISO-IP (International Standards Organization Internet Protocol)
81-VMTP
82-SECURE-VMTP
83-VINES
84-TTP
85-NSFNET-IGP (National Science Foundation Network Interior Gateway Protocol)
86-DGP (Dissimilar Gateway Protocol)
87-TCF
88-IGRP
89-OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
90-Sprite-RPC
91-LARP (Locus Address Resolution Protocol)
92-MTP (Multicast Transport Protocol)
94-IPIP (IP-within-IP Protocol)
95-MICP (Mobile Internetworking Control Protocol)
96-SCC-IP (Semaphore Communications Security Protocol)
97-ETHERIP (Ethernet-within-IP Protcol)
98-ENCAP (Encapsulation Header)
99-Any private encryption scheme
100-GMTP
101-254-Unassigned
255-Reserved
Example: set protocol=94
Location: Filter filter-name > Input-Filters > IP-Filter,
Filter filter-name > Output-Filters > IP-Filter
See Also: Input-Filters, IP-Filter, Output-Filters, Type
Proxy-Mode
Description: Specifies how the MAX TNT uses proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) on
the interface.
Because devices use ARP for local addresses, Proxy-Mode applies to WAN links only when the remote device is dynamically assigned an IP address that appears to be on the local network. The MAX TNT knows that packets addressed to that host must be routed across the WAN, but to other local routers and hosts, the address appears to be on the local network. Local TCP/IP software sees the IP address as local and sends out ARP requests.
You can turn on proxy mode to enable the MAX TNT to respond to ARP requests for "local" addresses that are actually across the WAN. When proxy mode is on, the MAX TNT responds with the interface's Media Access Control (MAC) address.
Usage: Specify one of the following values:
- Off (the default) specifies that the MAX TNT does not proxy any addresses.
- Active specifies that the MAX TNT uses proxy mode only for active connections.
- Inactive specifies that the MAX TNT uses proxy mode only for inactive connections.
- Always specifies that the MAX TNT uses proxy mode for all addresses.
Example: set proxy-mode=inactive
Location: IP-Interface
See Also: Atalk-Peer-Mode, RARP-Enabled
Q
Queue-Depth
Description: Specifies the queue depth for SNMP requests.
Usage: Specify a number from 0 to 1024. The default is 0 (zero), which means that the MAX
TNT does not drop packets, no matter how far behind the SNMP subsystem gets. If the queue
were to grow too large in a heavily loaded routing environment, the system could ultimately
run out of memory.
Example: set queue-depth=32
Location: SNMP
See Also: RIP-Queue-Depth
R
R2-Signaling-Enabled
Description: Indicates whether R2 signaling is enabled.
Usage: The R2-Signaling-Enabled setting is read only. Yes indicates that R2 signaling is
enabled. No indicates that R2 signaling is not enabled.
Example: r2-signaling-enabled=no
Location: Base
See Also: AIM-Enabled, Countries-Enabled, Data-Call-Enabled, D-Channel-Enabled,
Frame-Relay-Enabled, MAXLink-Client-Enabled, Modem-Dialout-Enabled,
Multi-Rate-Enabled, Switched-Enabled
Rad-Acct-Client
Description: A subprofile that enables you to define how the MAX TNT interacts as a client
to RADIUS accounting servers.
Usage: With External-Auth as the working profile, list the Rad-Acct-Client subprofile. For
example:
admin> list rad-acct-client
acct-server-1=0.0.0.0
acct-server-2=0.0.0.0
acct-server-3=0.0.0.0
acct-port=0
acct-src-port=0
acct-key=""
acct-timeout=0
acct-sess-interval=0
acct-id-base=acct-base-10
acct-limit-retry=0
acct-drop-stop-on-auth-fail=no
acct-stop-only=yes
You can then use the Set command to modify the settings in the subprofile. To close the subprofile and return to a higher context in the working profile:
admin> list ..
Location: External-Auth
See Also: Acct-Drop-Stop-On-Auth-Fail, Acct-ID-Base, Acct-Key, Acct-Limit-Retry,
Acct-Port, Acct-Server-N (N=1-3), Acct-Sess-Interval, Acct-Src-Port, Acct-Stop-Only,
Acct-Timeout
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


techpubs@eng.ascend.com
Copyright © 1998, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights
reserved.

