
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


Configuring Ethernet Cards
This chapter covers the following topics:
Introduction
This chapter explains how to install and configure the Ethernet card in the MAX TNT. For information about configuring IP routing, see the MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide.
There are two different Ethernet cards available for the MAX TNT:
- 10 Mbps Ethernet card
- 10/100 Mbps Ethernet card
10 Mbps Ethernet card
The 10 Mbps Ethernet card is single-height, with four 10Base-T Ethernet interfaces. This card provides full 10 Mbps access to up to four Ethernet networks.
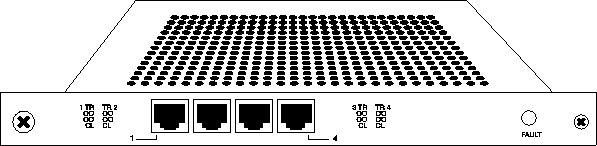
Figure 5-1. 10 Mbps Ethernet card
10/100 Mbps Ethernet card
The 10/100 Mbps Ethernet card is single-height, with four 10Base-T Ethernet interfaces and one 100Base-T Ethernet interface. This card provides full 10 Mbps access to up to four Ethernet networks and 100 Mbps access for a single Ethernet network.
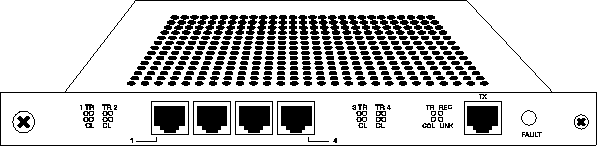
Figure 5-2. 10/100 Mbps Ethernet card
Installing the Ethernet card
You install Ethernet cards in the same way you install other MAX TNT slot cards. For information about installing MAX TNT slot cards, see Installing a slot card.
Overview of Ethernet configuration
Each of the Ethernet cards provides multi-port Ethernet routing capabilities. The configuration of each port on the card is identical to the configuration of the Ethernet port on the shelf controller. For complete information about configuring the Ethernet ports for routing, see the MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide.
All MAX TNT systems have an Ethernet port on the shelf-controller. This Ethernet port is designed for out-of-band management and light traffic loads. It is not intended to be the primary Ethernet interface for the system. If your MAX TNT will be routing heavy Ethernet traffic, use an Ethernet card.
Table 5-1 lists the sections describing common tasks you might have to perform to configure an Ethernet card. The table includes some descriptive information about each task, and lists the associated parameters and commands. (For complete information about the associated parameters, see the MAX TNT Reference Guide. )
To configure the shelf-controller Ethernet port see Performing Basic Configuration.
Understanding the Ethernet-related profiles
The MAX TNT creates the following profiles when it detects an Ethernet port:
- Ethernet profile
- IP-Interface profile
- SNMP profiles (Admin-State and a Device-State profile)
For an explanation of SNMP profiles, see the MAX TNT Adminstration Guide.
Ethernet profile
The MAX TNT creates a default Ethernet profile for each Ethernet port it detects, including the shelf controller. The Ethernet profile specifies the link-layer configuration for the port.
For example, when you display the profile for an Ethernet card installed in slot 4, you see a screen similar to the following:
admin> dir ether
8 02/15/1997 14:41:53 { shelf-1 controller 1 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 1 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 2 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 3 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 4 }
If the 10/100 Mbit card is installed, the 100 Mbit Ethernet port shows up as port 5. For example:
admin> dir ether
8 02/15/1997 14:41:53 { shelf-1 controller 1 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 1 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 2 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 3 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 4 }
16 02/17/1997 11:27:02 { shelf-1 slot-4 5 }
IP-Interface profile
The MAX TNT creates a default IP-Interface profile for each Ethernet port it detects, including the shelf controller. You can create multiple IP interfaces for each physical Ethernet port, but the default IP-Interface profile must have an IP address, or the other IP-Interface profiles for the same port will not function.
Assigning an IP address to the Ethernet port
To assign an IP address to the Ethernet port:
- Read in the IP-Interface profile for the Ethernet port you want to configure. For example,
if you want to configure the Ethernet port in shelf 1, slot 15, port 1:
admin> read ip-interface {{1 15 1 } 0}
- Set the IP address:
admin> set ip-address=ip address
- Write the profile:
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-15 1 } 0 } written
Understanding names in the interface table
The interface table entries associated with an Ethernet card have the following components:
ie shelf-slot-item
For example, a four-port Ethernet card in slot 13 appears as four entries in the interface table, one for each Ethernet interface:
admin> netstat -in
Name MTU Net/Dest Address Ipkts Ierr Opkts Oerr
ie0 1500 192.168.6.0/24 192.168.6.122 2188408 27 1802 0
lo0 1500 127.0.0.1/32 127.0.0.1 0 0 0 0
rj0 1500 127.0.0.2/32 127.0.0.2 0 0 0 0
bh0 1500 127.0.0.3/32 127.0.0.3 0 0 0 0
ie1-13-1 1500 10.122.71.0/24 10.122.71.1 820642 0 819054 0
ie1-13-2 1500 10.122.72.0/24 10.122.72.1 819053 0 820642 0
ie1-13-3 1500 10.122.73.0/24 10.122.73.1 819602 0 900819 0
ie1-13-4 1500 10.122.74.0/24 10.122.74.1 900818 0 819602 0
Assigning a filter to the Ethernet interface
The only read-write parameter in an Ethernet profile is the Filter-Name parameter, which enables you to specify a data filter that affects which packets are allowed to reach this Ethernet interface or leave it for another interface. To apply a data filter to an Ethernet interface, you must first define the filter as described in MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide.
Note: Use caution when applying a filter to the Ethernet interface. You could inadvertently
render the MAX TNT inaccessible from the local LAN.
To assign a filter to the Ethernet profile:
- Read the Ethernet profile. For example:
admin> read ether {1 4 1}
ETHERNET/{ shelf-1 slot-4 1 } read
- Specify the filter name:
admin> set filter-name= filter name
ETHERNET/{ shelf-1 slot-4 1 } read
- Write the profile:
admin> write
ETHERNET/{ shelf-1 slot-15 1 } written
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


techpubs@eng.ascend.com
Copyright © 1997, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights
reserved.


