
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


Setting Up AppleTalk Connections
This chapter describes how to configure a RADIUS user profile for AppleTalk connections. The chapter is divided into the following sections:
Before you begin
Before configuring a RADIUS user profile for an AppleTalk connection, you must set carry out the following tasks:
- Set Enabled=Yes in the ARA-Answer subprofile of the Answer-Defaults profile.
- Configure parameters in the Atalk-Interface profile.
Depending on your network configuration, you might be required to perform the following additional tasks:
- If you intend to allow ARA Guest access, set Profiles-Required=No in the Answer-Defaults profile. Setting Profiles-Required=Yes disables ARA Guest access.
- If AppleTalk clients will dial into the MAX TNT, define a virtual AppleTalk network by setting parameters in the Atalk-Global profile. The MAX TNT must be able to assign dial-in clients an AppleTalk address from a pool of addresses, and can do so only if you configure the Atalk-Global profile with a network range.
For complete information, see the MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide.
Overview of AppleTalk connections
A MAX TNT configured for AppleTalk routing enables dial-in connections from AppleTalk Remote Access (ARA) client software, PPP dial-in software that supports AppleTalk, and AppleTalk-enabled Ascend units.
Figure 5-1 shows a MAX TNT that routes AppleTalk between WAN interfaces and a local AppleTalk interface.
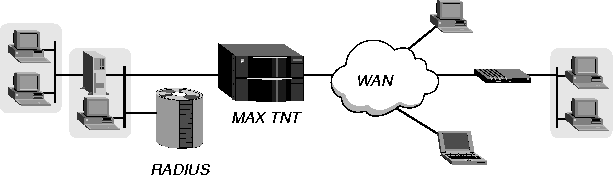
Figure 5-1. Routing AppleTalk between LAN and WAN interfaces
For a pure AppleTalk connection, a Macintosh user must have ARA Client software and an asynchronous modem. For a TCP/IP connection through ARA, the Macintosh must also be running TCP/IP software such as MacTCP or Open Transport.
PPP and ARA are the encapsulation protocols used for AppleTalk dial-in on the MAX TNT. Both ARA and PPP are supported in ARA 3.0. You can use AppleTalk PPP and ARA over a modem or V.120 ISDN TA connection. You can also use AppleTalk PPP over synchronous PPP when the calling unit is an Ascend router.
ARA is an asynchronous protocol. It supports V.120 and modem calls only. It does not support V.110 calls or synchronous connections. In addition, ARA does not support PAP or CHAP authentication.
Configuring an AppleTalk connection
To configure an AppleTalk connection in RADIUS, use the attributes listed in Table 5-1.
To configure an AppleTalk connection in a RADIUS user profile, proceed as follows:
- Specify a user name by setting the User-Name attribute, and a password by setting the
Password attribute.
- On any line other than the first one, set Framed-Protocol=ARA (for an ARA connection)
or Framed-Protocol=PPP (for an AppleTalk PPP connection).
- Set the Ascend-Ara-PW attribute to the same value specified by the Password attribute.
The MAX TNT requires both the Password and the Ascend-Ara-PW attributes. The ARA
software in the Ascend unit uses DES to encrypt and decrypt the ARA password.
- For a TCP/IP connection through ARA, turn on IP routing by setting
Ascend-Route-IP=Route-IP-Yes.
- If the MAC TCP/IP software has a hard-coded IP address, set the Framed-Address
attribute (and, optionally, the Framed-Netmask attribute) to specify the Macintosh user's
IP address.
- If the MAC TCP/IP software expects a dynamic IP address assignment, set up dynamic IP
addressing as described in Defining a pool of addresses for dynamic assignment. Then, set
the Ascend-Assign-IP-Pool attribute in the user profile to specify the address pool from
which RADIUS should assign the user an address.
Example of configuring a user profile for an ARA client
In Figure 5-2, the dial-in client is running ARA 3.0, with ARA encapsulation selected and an internal modem.
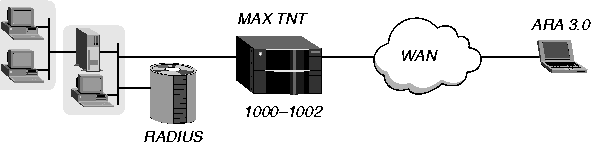
Figure 5-2. Configuring ARA client dial-in
In this example, the client will be assigned a network address on the virtual 1000-1002 network defined by the Atalk-Global profile. You would configure the user profile as follows:
Emma Password="pwd"
Framed-Protocol=ARA,
Ascend-Ara-PW="pwd"
Example of configuring an AppleTalk PPP dial-in connection
An AppleTalk PPP dial-in client connection uses the PPP encapsulation protocol. In Figure 5-3, the dial-in client is running ARA 3.0, and has selected PPP encapsulation.
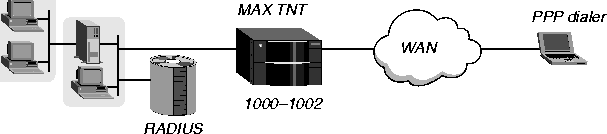
Figure 5-3. AppleTalk connection using a PPP dialer
The client will be assigned a network address on the virtual 1000-1002 network defined by the Atalk-Global profile. You would configure the user profile as follows:
Emma Password="pwd"
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Ascend-Ara-PW="pwd"
Example of configuring an ARA client connection for DDP-IP tunneling
A DDP-IP gateway adds DDP encapsulation to IP packets it transmits, and removes DDP from IP packets it receives. This function enables the use of ARA client software for IP connections, provided that the Macintosh TCP/IP software is configured properly, as described in Table 5-2.
Table 5-2. Macintosh software configuration
Macintosh software
|
Settings
|
|---|
|
Open Transport
|
The TCP/IP Control Panel can be set to Mac-IP (for ARA connections) or PPP (for AppleTalk PPP). MacIP is required for DDP-IP encapsulation. The Control Panel also has an option to configure its IP address manually, via BootP, DHCP, or RARP. In this example, where the Macintosh has a host route, choose Manually and enter the IP address. In another situation, the MAX TNT can assign an address to the Macintosh from a pool of allocated addresses, in which case the Control Panel should specify BootP.
|
|
MacTCP
|
The MacTCP Control Panel should have an icon for ARA. That icon must be selected for DDP-IP encapsulation. The Control Panel also has an option to configure its IP address manually or from a Server. In this example, where the Macintosh has a host route, choose Manually and enter the IP address. In another situation, the MAX TNT can assign an address to the Macintosh from a pool of allocated addresses, in which case the Control Panel should specify Server. Do not choose "Dynamically" in the MacTCP Control Panel. That option is not supported.
|
In Figure 5-4, the dial-in client is running ARA 3.0 (which includes DDP-IP tunneling capabilities) and an IP application such as Telnet to communicate with an IP host on the MAX TNT local interface. The client has its own host route.
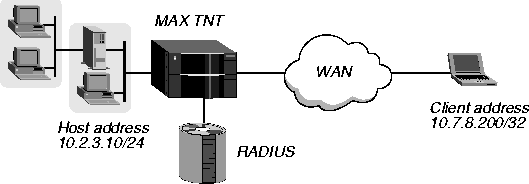
Figure 5-4. DDP-IP connection using ARA 3.0
The MAX TNT must be configured as an IP router as well as an AppleTalk router. For details about configuring the IP router, see the MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide.
The following sample configuration enables the client to dial in using ARA client 3.0 and then initiate a Telnet connection to a host on the MAX TNT unit's IP network:
Emma Password="pwd"
Framed-Protocol=ARA,
Ascend-Ara-PW="pwd",
Framed-Address=10.7.8.200,
Framed-Netmask=255.255.255.0,
Ascend-Route-IP=Route-IP-Yes,
Framed-Route="10.2.3.10/24 0.0.0.0/0 1 n ara-out"
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


techpubs@eng.ascend.com
Copyright © 1998, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights
reserved.

