
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


Setting Up PPP, MP, and MP+ Connections
This chapter describes how to configure a RADIUS user profile for PPP, MP, and MP+ connections. The chapter is divided into the following sections:
- Before you begin
|
- Overview of PPP, MP, and MP+
|
- Overview of PPP, MP, and MP+ configuration tasks
|
- Setting up a dial-in PPP, MP, or MP+ connection
|
- Setting up an outgoing PPP, MP, or MP+ connection
|
- Setting up a Nailed/MPP connection
|
- Setting up a nailed-up connection
|
- Managing bandwidth
|
- Limiting access to devices and services
|
- Restricting access to ports, lines, and channels
|
- Setting up disconnects
|
Before you begin
Before configuring the RADIUS user profile for a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection, perform the following tasks at the MAX TNT configuration interface:
- Specify system-wide settings.
- Enable the appropriate encapsulation method(s).
- Specify an authentication protocol.
- Set up the MAX TNT to accept client requests.
The sections that follow briefly describe each task. For complete information, see the MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide.
Specifying system-wide settings
To specify system-wide settings:
- In the System profile, indicate the MAX TNT unit's name with the Name parameter. You
can specify up to 24 characters. The default value is null.
- If you want the MAX TNT to add channels to an MP+ call in multiples, rather than one at
a time, set the System Profile's Parallel-Dialing parameter to a number greater than 1. The
Parallel-Dialing parameter determines how many calls the unit can dial out concurrently.
- Decide whether the MAX TNT should use the Answer-Defaults profile as the default
when answering a call. If so, set Use-Answer-For-All-Defaults=Yes in the
Answer-Defaults profile. If you accept the default setting of No, the MAX TNT uses the
factory defaults.
Enabling the encapsulation method
When setting up your connection, select the appropriate encapsulation method(s) in a subprofile of the Answer-Defaults profile. Proceed as follows:
- To enable the MAX TNT to answer a single-channel PPP call, set PPP-Enabled=Yes in the
PPP-Answer subprofile.
- To enable the MAX TNT to answer an MP call, set Enabled=Yes in the MP-Answer
subprofile.
- To enable the MAX TNT to answer a multichannel MP+ call, set Enabled=Yes in the
MPP-Answer subprofile.
Specifying an authentication protocol
If you choose, you can specify an authentication protocol for name and password authentication of PPP, MP, and MP+ calls. In the Answer-Defaults profile's PPP-Answer subprofile, set the Receive-Auth-Mode parameter to PAP-PPP-Auth, CHAP-PPP-Auth, MS-CHAP-PPP-Auth, or Any-PPP-Auth. (For descriptions of these settings, see Table 3-5.)
If the incoming PPP call does not include a source IP address, the MAX TNT requires PAP, CHAP, or MS-CHAP authentication.
Setting up the MAX TNT to accept client requests
If you plan to configure RADIUS to accept disconnect requests, you must specify settings in the Rad-Auth-Server subprofile of the External-Auth profile. For information about how to carry out this task, see Configuring the MAX TNT for RADIUS client requests.
Overview of PPP, MP, and MP+
This section provides a brief introduction to PPP, MP, and MP+ connections. For complete information, see the MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide.
What is PPP?
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) enables dial-in connections from an analog modem or ISDN device that uses a single channel, and supports single-channel dialout connections. The connection can be asynchronous or synchronous.
Figure 4-1 shows a single-channel asynchronous PPP call from a remote user running Windows 95 with the TCP/IP stack and PPP dialup software. The calling device is a modem. The MAX TNT uses Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) or Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) to authenticate the connection.
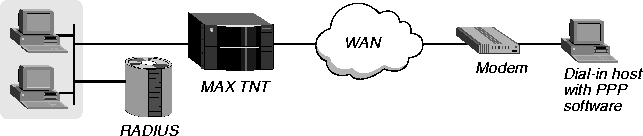
Figure 4-1. Asynchronous PPP connection
If the caller uses an analog modem, as in Figure 4-1, the connection can use PPP and PAP, CHAP, or MS-CHAP authentication, but the MAX TNT handles the call as a terminal-server connection. The MAX TNT routes the call to a digital modem, which passes the call to the terminal-server software. When the terminal server recognizes PPP encapsulation in the call, it passes the call to the router software.
The connection shown in Figure 4-2 is a single-channel synchronous PPP call that uses CHAP authentication. The remote-end device is a Pipeline unit with the IP address 10.2.3.31/24.
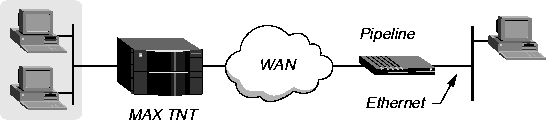
Figure 4-2. Synchronous PPP connection
If the caller is an ISDN device, as in Figure 4-2, the connection can use terminal server, PAP, CHAP, or MS-CHAP authentication.
What is MP?
Multilink Protocol (MP) uses the encapsulation defined in RFC 1990, and enables the MAX TNT to interact with MP-compliant equipment from other vendors. MP supports multichannel links, but not Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA). The base channel count determines the number of calls to place, and the number of channels does not change.
The MP connection shown in Figure 4-3 is allocated two channels. It uses MP encapsulation and CHAP authentication.
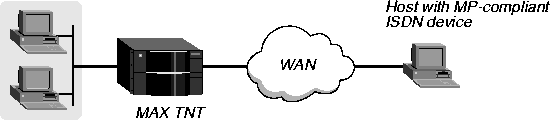
Figure 4-3. MP connection
MP requires that all channels in the connection share the same phone number. That is, the channels on the answering side of the connection must be in a hunt group. Both sides of the link must support MP encapsulation.
What is MP+?
Multilink Protocol Plus (MP+) uses PPP encapsulation with Ascend extensions, and enables the MAX TNT to connect to another Ascend unit with multiple channels. MP+ supports Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA), enabling the MAX TNT to increase bandwidth as necessary and to drop bandwidth when the connection no longer requires it. The criteria for adding or dropping a link are determined by Ascend extensions and are supported only by Ascend equipment. An MP+ connection can combine up to 30 channels into a single high-speed connection.
Figure 4-4 shows the MAX TNT connected to a remote Pipeline 25 with an incoming MP+ connection.
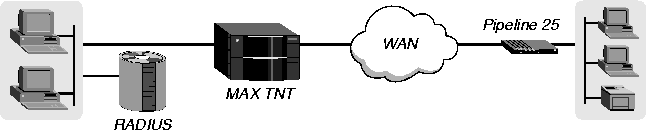
Figure 4-4. MP+ connection
Other types of units might support MP but not MP+. So, if you configure an MP+ connection in RADIUS between the MAX TNT and a non-Ascend unit, the MAX TNT first requests the MP+ protocol. If the remote device refuses MP+, the MAX TNT uses MP instead. If the answering device refuses both MP+ and MP, the MAX TNT sets up a PPP call on a single channel.
Overview of PPP, MP, and MP+ configuration tasks
When you configure a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection, you must:
Depending on the nature of your dial-in connection, you might also need to carry out the following additional tasks:
- Configure a Nailed/MPP connection, as described in Setting up a Nailed/MPP connection.
- Configure a nailed-up connection, as described in Setting up a nailed-up connection.
- Manage bandwidth for the connection, as described in Managing bandwidth.
- Limit the devices and services the caller can use, as described in Limiting access to devices and services.
- Limit the ports, lines, and channels the caller can use, as described in Restricting access to ports, lines, and channels.
- Configure disconnects for certain users and sessions, as described in Setting up disconnects.
Setting up a dial-in PPP, MP, or MP+ connection
When you configure a dial-in PPP, MP, or MP+ connection, you must carry out the following tasks:
- Set the User-Name, Password, and User-Service attributes.
- Set the Framed-Protocol attribute.
- Set the Framed-Address attribute (and Framed-Netmask if a subnet mask is in use).
For complete information about performing the required tasks, see Configuring required attributes for a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection.
Depending on your configuration, you also have the option of specifying:
- IP address of the MAX TNT
- Async control character map
- Maximum packet size
- Compression settings
For complete information about performing the optional tasks, see Configuring optional attributes for a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection.
Overview of PPP, MP, and MP+ attributes
To configure a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection in RADIUS, use the attributes listed in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1. PPP, MP, and MP+ attributes
Attribute
|
Description
|
Possible values
|
|---|
|
Ascend-Link-Compression (233)
|
Turns data compression on or off.
|
Link-Comp-None (0) disables data compression.
Link-Comp-Stac (1) enables Ascend's modified version of the STACKER LZS compression/decompression algorithm.
Link-Comp-Stac-Draft-9 (2) enables the STACKER LZS compression/decompression algorithm, as specified in draft 9 of the IETF draft PPP Stac LZS Compression Protocol.
Link-Comp-MS-Stac (3) enables Microsoft's modified version of the STACKER LZS compression/decompression algorithm.
Link-Comp-None is the default.
|
|
Ascend-PPP-Address (253)
|
Specifies the IP address of the MAX TNT as reported to the calling unit during PPP IPCP negotiations.
|
IP address in dotted decimal notation n.n.n.n, where n is a number from 0 to 255.
The default value is 0.0.0.0.
|
|
Ascend-PPP-Async-Map (212)
|
Provides the async control character map for the session.
|
Four-byte bitmap to one or more control characters. The default is the standard async control character.
|
|
Ascend-PPP-VJ-1172 (211)
|
Instructs the MAX TNT to use the 0037h value for the VJ compression type.
RFC 1172 section 5.2 contains an erroneous statement that the VJ compression type value is 0037h. It should be 002dh. However, many older implementations use the 0037h value when negotiating VJ compression.
|
You can specify PPP-VJ-1172 to indicate 0037h. If you do not specify this value, RADIUS uses the default-VJ compression type 002dh.
|
|
Ascend-PPP-VJ-Slot-Comp (210)
|
Specifies whether the MAX TNT uses slot compression when sending VJ-compressed packets.
|
VJ-Slot-Comp-No (0)
VJ-Slot-Comp-Yes (1)
VJ-Slot-Comp-Yes is the default.
|
|
Framed-Address (8)
|
Specifies the IP address of the remote user or calling device.
|
IP address in dotted decimal notation n.n.n.n, where n is a number from 0 to 255.
The default value is 0.0.0.0.
|
|
Framed-Compression (13)
|
Turns on TCP/IP header compression. This setting applies only to packets in TCP applications, such as Telnet, and turns on header compression for both sides of the link.
|
You can specify Van-Jacobson-TCP-IP to turn on TCP/IP header compression. If you do not specify this value, RADIUS uses the default of no header compression.
|
|
Framed-MTU (12)
|
Specifies the maximum number of bytes the MAX TNT can receive in a single packet on a link.
|
Integer from 1 to 1524. The default value is 1524.
|
|
Framed-Netmask (9)
|
Specifies the subnet mask associated with the IP address of a station or router at the remote end of the link.
|
IP address in dotted decimal notation n.n.n.n, where n is a number from 0 to 255. The default value is 0.0.0.0.
|
|
Framed-Protocol (7)
|
Specifies the type of protocol the link can use.
|
PPP (1)
SLIP (2)
ARA (255)
MPP (256)
FR (261)
FR-CIR (263)
By default, the MAX TNT does not restrict the type of protocol a link can use.
|
|
Password (2)
|
Specifies the user's password.
|
Alphanumeric string of up to 252 characters. The default value is null.
|
|
User-Name (1)
|
Specifies the name of the remote user or device.
|
Alphanumeric string of up to 252 characters. The default value is null.
|
|
User-Service (6)
|
Specifies whether the link can use framed or unframed services.
|
Login-User (1)
Framed-User (2)
Dialout-Framed-User (5)
By default, the MAX TNT does not restrict the services that a link can use.
|
Configuring required attributes for a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection
To configure a dial-in PPP, MP, or MP+ connection in a RADIUS user profile, you must set:
- User-Name, Password, and User-Service attributes
- Framed-Protocol attribute
- Framed-Address attribute (and Framed-Netmask if a subnet mask is in use)
Setting the User-Name, Password, and User-Service attributes
On the first line of the RADIUS user profile:
- For User-Name, specify the name of the dial-in user or device.
- For Password, specify the dial-in caller's password.
- Set User-Service=Framed-User.
Setting the Framed-Protocol attribute
To specify that the caller must use PPP, MP, or MP+, set Framed-Protocol=PPP on any line other than the first. A user requesting access can dial in with PPP, MP, or MP+ framing. Or, the user can dial in unframed, and then change to PPP framing. If the user dials in with any other type of framing, the MAX TNT rejects the call.
Setting the Framed-Address attribute
On any line other than the first, set the Framed-Address attribute to the IP address of the caller. If a subnet mask is in use, specify it by setting the Framed-Netmask attribute as well.
Configuring optional attributes for a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection
When configuring a dial-in PPP, MP, or MP+ connection, you have the option of specifying:
- IP address of the MAX TNT
- Async control character map
- Maximum packet size
- Compression settings
Specifying the MAX TNT unit's IP address
To specify the MAX TNT unit's IP address, set the Ascend-PPP-Address attribute.
If you specify a valid IP address, IPCP negotiates with that IP address. If you set the value of this attribute to 255.255.255.255, IPCP negotiates with the address 0.0.0.0. Note that you can assign Ascend-PPP-Address a value different from the MAX TNT unit's true IP address, as long as the user requesting access is aware of the discrepancy.
If you accept the default value of 0.0.0.0, IPCP negotiates using the value of the IP-Address and Netmask values in the IP-Interface profile.
Specifying the async control character map
To specify the async control character map for the session, set the Ascend-PPP-Async-Map attribute.
The value you specify is a four-byte bitmap to one or more control characters. The async control character map is defined in RFC 1548, and specifies that each bit position represents one of the 32 ASCII control characters. The bits are ordered with the lowest bit of the lowest byte being 0 (zero). For example, bit 19 corresponds to Control-S (DC3) or ASCII 19. The control characters pass through the link as data. Only applications running over the link use the data.
Specifying the maximum packet size
To specify the maximum number of bytes the MAX TNT can receive in a single packet on a link, set the Framed-MTU attribute.
The default value is 1524. You should accept this default unless the device at the remote end of the link cannot support it. If the administrator of the remote network specifies that you must change this value, specify a number from 1 to 1524.
Specifying compression settings
To specify compression settings, proceed as follows:
- To turn on data compression, set Ascend-Link-Compression to a value other than
Link-Comp-None. Both sides of the link must turn on data compression for this setting to
have any effect.
- To turn on TCP/IP header compression, set Framed-Compression=Van-Jacobson-TCP-IP.
Turning on header compression is most effective in reducing overhead when the data
portion of the packet is small.
When you specify this setting, the MAX TNT removes the TCP/IP header, and associates a TCP/IP packet with a connection by giving it a slot ID. The first packet coming into a connection must have a slot ID, but succeeding packets need not have one. If the packet does not have a slot ID, the MAX TNT associates it with the last-used slot ID. This scenario uses slot ID compression, because the slot ID does not appear in any packet but the first in a stream.
- If Framed-Compression=Van-Jacobson-TCP-IP, you can instruct the MAX TNT not to use
slot compression by setting Ascend-PPP-VJ-Slot Comp=VJ-Slot-Comp-No. When you
specify this setting, each VJ-compressed packet has a slot ID.
- To instruct the MAX TNT to use the 0037h value for the VJ compression type, set
Ascend-PPP-VJ-1172=PPP-VJ-1172.
Example of configuring a connection that uses MP+
In Figure 4-5, the MP+ connection uses link compression, TCP/IP header compression, and IP routing for an incoming call from the user Emma at IP address 200.250.55.9.
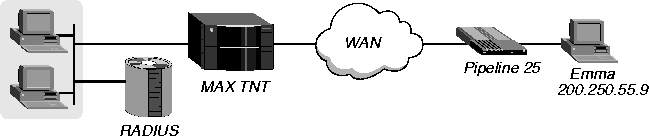
Figure 4-5. Configuring an MP+ connection
In the example, you would configure Emma's user profile as follows:
Emma Password="m2dan", User-Service=Framed-User
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Framed-Address=200.250.55.9,
Framed-Netmask=255.255.255.248,
Ascend-Link-Compression=Link-Comp-Stac,
Framed-Compression=Van-Jacobson-TCP-IP,
Ascend-Route-IP=Route-IP-Yes,
Ascend-Metric=2
Setting up an outgoing PPP, MP, or MP+ connection
To configure outgoing calls in a RADIUS user profile, you must specify:
- User name, password, and user service
- Telephone number the MAX TNT dials
- IP address and subnet mask (if dynamic IP addressing is not in use)
Depending on your configuration, you also have the option of specifying:
- Encapsulation method
- Data service
- Billing number
- Type of T1 PRI service
- Type of phone number for T1 PRI calls
- U.S. Interexchange Carrier (IEC) for long-distance T1 PRI calls
Overview of outgoing-call attributes
To configure outgoing calls in RADIUS, use the attributes listed in Table 4-2.
Table 4-2. Outgoing call attributes
Attribute
|
Description
|
Possible values
|
|---|
|
Ascend-Billing-Number (249)
|
Specifies a billing number for charges you incur on the line. If you do not enter a billing number, the telephone company assigns charges to the telephone number associated with the line.
|
Up to ten characters, limited to the following:
1234567890()[]!z-*# |
The default value is null.
|
|
Ascend-Call-By-Call (250)
|
Specifies the T1 PRI service that the MAX TNT uses when placing a PPP call.
|
Integer corresponding to services provided by AT&T, MCI, and Sprint. By default, the MAX TNT uses ACCUNET Switched Digital Services from AT&T (6).
|
|
Ascend-Data-Svc (247)
|
Specifies the type of data service the link uses for outgoing calls.
|
For a complete list of possible values, see Ascend-Data-Svc (247).
When you set the Ascend-Data-Svc attribute to Switched-Modem, a user cannot connect to the MAX TNT with ISDN and is restricted to analog access.
Setting Ascend-Data-Svc=Switched-64K enables the user to connect to any and all data services.
Switched-56K is the default.
|
|
Ascend-Dial-Number (227)
|
Specifies the phone number the MAX TNT dials to reach the router or node at the remote end of the link.
|
Up to 21 characters, limited to the following:
1234567890()[]!z-*#|
The default value is null.
|
|
Ascend-PRI-Number-Type (226)
|
Specifies the type of phone number the MAX TNT dials.
|
Unknown-Number (0)
Intl-Number (1)
National-Number (2)
Local-Number (4)
Abbrev-Number (5)
National-Number is the default.
|
|
Ascend-Transit-Number (251)
|
Specifies the U.S Interexchange Carrier (IEC) you use for long distance calls over a T1 PRI line.
|
Integer corresponding to an IEC. The default value is null.
|
|
Framed-Address (8)
|
Specifies the IP address of the called device.
|
IP address in dotted decimal notation n.n.n.n, where n is a number from 0 to 255. The default value is 0.0.0.0. An answering user profile with this setting matches all IP addresses.
|
|
Framed-Netmask (9)
|
Specifies the subnet mask in use for the called device.
|
IP address in dotted decimal notation n.n.n.n, where n is a number from 0 to 255. The default value is 0.0.0.0.
|
|
Framed-Protocol (7)
|
Specifies the type of protocol the link can use.
|
PPP (1)
SLIP (2)
ARA (255)
MPP (256)
FR (261)
FR-CIR (263)
When User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User, the Framed-Protocol attribute specifies the type of framing allowed on the outgoing call.
By default, the MAX TNT does not restrict the type of protocol a link can use.
|
|
Password (2)
|
Specifies the user's password.
|
Alphanumeric string of up to 252 characters. The default value is null.
|
|
User-Name (1)
|
Specifies the name of the remote user or device.
|
Alphanumeric string of up to 252 characters. The default value is null.
|
|
User-Service (6)
|
Specifies whether the link can use framed or unframed services.
|
Login-User (1)
Framed-User (2)
Dialout-Framed-User (5)
By default, the MAX TNT does not restrict the services that a link can use.
|
Configuring required outgoing call attributes
To set up an outgoing call in a RADIUS user profile, you must specify a user name and password, a user service, and the telephone number the MAX TNT dials. If dynamic IP addressing is not in use, you must also specify an IP address and subnet mask.
Specifying a name, password, and user service for outgoing calls
On the first line of the user profile, proceed as follows:
- Set the User-Name attribute to the name of the remote device that will receive outgoing calls, and append -Out to the user name.
- Set the Password attribute to "ascend".
- Set User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User. This setting ensures that no one can use the profile for authentication of an incoming call.
Then, on the second line of the profile, set the User-Name attribute to the name of the remote device that will receive outgoing calls.
For example, you might enter the first two lines in the profile for the remote device Homer as follows:
Homer-Out Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User
User-Name="Homer",
Specifying the phone number the MAX TNT dials
To indicate the phone number the MAX TNT dials to reach the router or node at the remote end of the link, set the Ascend-Dial-Number attribute. The MAX TNT sends only the numeric characters to place a call. If Use-Trunk-Groups=Yes in the System profile, the first digits in the Ascend-Dial-Number attribute have the meanings listed in Table 4-3.
Specifying an IP address and subnet mask
Specify the called device's IP address with the Framed-Address attribute. If a subnet is in use, you must also specify a value for the Framed-Netmask attribute.
If you specify an IP address, you must also enable IP routing for the profile by setting Ascend-Route-IP=Route-IP-Yes. (For more information, see Enabling IP routing.)
Configuring optional outgoing call attributes
When you configure an outgoing call, you can specify the encapsulation method and data service the call should use, and a billing number for the line. You can also determine whether the MAX TNT waits for the remote unit to call back. In addition, if you are using a T1 PRI line, you can specify the type of phone number, T1 PRI service, and long-distance service the call uses.
Specifying an encapsulation method for an outgoing call
To specify the encapsulation method in use for the call, set the Framed-Protocol attribute. For PPP calls, set Framed-Protocol=PPP. For MP+ calls, set Framed-Protocol=MPP.
Specifying a data service
To specify the data service the link uses for outgoing calls, set the Ascend-Data-Svc attribute. For a complete list of the values you can specify, see Ascend-Data-Svc (247).
Specifying a billing number
To indicate a billing number for charges you incur on the line, set the Ascend-Billing-Number attribute. If you do not enter a billing number, the telephone company assigns charges to the telephone number associated with the line. Your carrier determines the billing number, and uses it to sort your bill. If you have several departments, and each department has its own billing number, your carrier can separate and tally each department's usage.
The MAX TNT uses the Ascend-Billing-Number value differently depending on the type of line you use:
- For a T1 line, the MAX TNT appends the value specified in the Ascend-Billing-Number attribute to the end of each phone number it dials for the call.
- Ascend-Billing-Number for outgoing calls applies only to installations in Australia.
- For a T1 PRI line, the MAX TNT uses the Ascend-Billing-Number attribute, rather than the phone number ID, to identify itself to the answering party.
Specifying the T1 PRI service
To specify the T1 PRI service that the MAX TNT uses, set the Ascend-Call-By-Call attribute. Specify a number corresponding to the type of service the MAX TNT uses. Table 4-4 lists the services available for each service provider.
Specifying the type of number the MAX TNT dials (T1 PRI only)
To specify the type of phone number the MAX TNT dials, set the Ascend-PRI-Number-Type attribute to one of the settings listed in Table 4-5.
Specifying the long-distance carrier (T1 PRI only)
To specify the U.S. Interexchange Carrier (IEC) you use for long distance calls over a T1 PRI line, set the Ascend-Transit-Number attribute. Specify the same digits you use to prefix a phone number you dial over a T1 access line or voice interface:
- 288 selects AT&T.
- 222 selects MCI.
- 333 selects Sprint.
The default value is null. If you accept the default, the MAX TNT uses any available IEC for long-distance calls.
Example of configuring an outgoing MP+ call
In Figure 4-6, a user dials a call from the MAX TNT at the local end to a MAX TNT at the remote end.
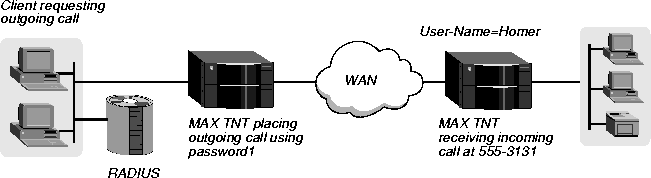
Figure 4-6. Configuring an outgoing MP+ call
To enable IP traffic to initiate a call to a MAX TNT called Homer, and to have the connection request PAP authentication, you would configure the pseudo-user profile as follows:
Homer-Out Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User
User-Name="Homer",
Ascend-Dial-Number=555-3131,
Framed-Protocol=MPP,
Framed-Address=10.0.100.1,
Framed-Netmask=255.255.255.0,
Ascend-Metric=2,
Framed-Routing=None,
Ascend-Idle-Limit=30,
Ascend-PRI-Number-Type=National-Number,
Ascend-Send-Auth=Send-Auth-PAP,
Ascend-Send-Secret="password1"
Setting up a Nailed/MPP connection
A Nailed/MPP connection is a nailed-up connection that can add switched channels to increase bandwidth or to provide a backup if nailed-up channels are down. The maximum number of channels for the Nailed/MPP connection is the value of the Ascend-Maximum-Channels attribute or the number of nailed channels in the specified group, whichever is greater.
The base channels of a Nailed/MPP connection are nailed-up. If a nailed-up channel is temporarily down, the MAX TNT polls continuously trying to re-establish that connection. If the MAX TNT receives an outbound packet while the nailed-up connection is still down, the MAX TNT replaces that channel with a switched channel, even if the call is online with more than the minimum number of channels.
The MAX TNT adds or subtracts switched channels according to the Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) settings you make in the Connection profile or RADIUS profile. If the two sides of a connection disagree on the number of channels necessary for a connection, the side requesting the greater number prevails. Both sides make calculations on the required number of channels on the basis of the traffic each end receives.
Note: When the nailed portion of a Nailed/MPP connection is a Serial WAN (SWAN) line,
the MAX TNT does not calculate bandwidth usage, and so does not automatically add or
subtract switched channels on the basis of bandwidth usage.
Overview of Nailed/MPP attributes
To configure a Nailed/MPP connection in RADIUS, you must set the attributes listed in Table 4-6.
Configuring attributes for a Nailed/MPP connection
To configure a Nailed/MPP connection, set up a pseudo-user profile in the following manner:
- On the first line of the profile, specify the User-Name, Password, and User-Service
attributes in the following format:
permconn-name-num Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User
where name is the system name of the Ascend unit (the name specified by the Name parameter in the System profile), and num is a number in a sequential series, starting with 1.
- On the second line, specify the User-Name attribute to indicate the name of the device to
which the user makes the nailed-up connection.
- Set Framed-Protocol=MPP.
- Set the Framed-Address attribute to the IP address of the remote device.
- If a subnet mask is in use, set the Framed-Netmask attribute.
- Set Ascend-Call-Type=Nailed/Mpp.
- Set Ascend-FT1-Caller=FT1-Yes.
- Set the Ascend-Group attribute to specify the nailed-up channels the profile can use.
If a Nailed/MPP connection is down and the nailed channels are also down, the connection does not re-establish itself until the nailed channels come back up or one end dials the switched channels. (When the calling unit receives a packet whose destination is the unit at the remote end of the Nailed/MPP connection, the unit automatically dials the switched channels.)
- Set Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) attributes, as explained in Configuring DBA
in RADIUS.
- Set the Answer-Originate and FT1-Caller parameters for answering only in the remote
end's Connection profile.
Note: If you modify the RADIUS profile for a Nailed/MPP connection, most changes
become active only after the call goes down and then back up. However, if you add a group
number with the Ascend-Group attribute and save your changes, the MAX TNT adds the
channels to the connection without bringing it down.
Example of configuring a Nailed/MPP connection
In Figure 4-7, the MAX TNT establishes a Nailed/MPP connection with a Pipeline 25 across the WAN.
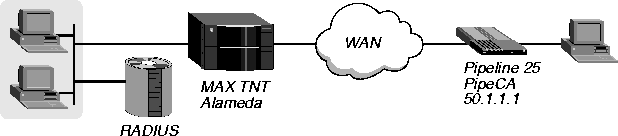
Figure 4-7. Configuring a Nailed/MPP connection
For a Nailed/MPP connection to use the nailed-up channels in groups 1, 3, 5, and 7, you would configure the pseudo-user profile as follows:
permconn-Alameda-1 Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User
User-Name="PipeCA",
Framed-Protocol=MPP,
Framed-Address=50.1.1.1,
Framed-Netmask=255.0.0.0,
Ascend-Route-IP=Route-IP-Yes,
Ascend-Metric=7,
Framed-Routing=None,
Ascend-Idle-Limit=0,
Ascend-Call-Type=Nailed/Mpp,
Ascend-Group="1,3,5,7",
Ascend-FT1-Caller=FT1-Yes,
Ascend-Target-Util=80,
Ascend-History-Weigh-Type=History-Constant,
Ascend-Seconds-Of-History=90,
Ascend-Add-Seconds=30,
Ascend-Remove-Seconds=30,
Ascend-Maximum-Channels=10,
Ascend-Inc-Channel-Count=2,
Ascend-Dec-Channel-Count=2,
Ascend-DBA-Monitor=DBA-Transmit-Recv
Setting up a nailed-up connection
A nailed-up connection is a permanent link that is always up as long as the physical connection persists. If the unit or central switch resets, or if the link goes down, the MAX TNT attempts to restore the link at ten-second intervals. If the MAX TNT or the remote unit is powered off, the link comes back up when the device boots up again. On an ISDN line, a nailed-up connection uses one or more channels. A serial WAN link is not divided into channels and is always 100% nailed up. The MAX TNT brings up any nailed connection retrieved from RADIUS.
Overview of nailed-up connection attributes
To configure a nailed-up connection in RADIUS, use the attributes listed in Table 4-7.
Configuring attributes for a nailed-up connection
To configure a nailed-up connection, set up a pseudo-user profile in the following manner:
- On the first line of the profile, specify the User-Name, Password, and User-Service
attributes in the following format:
permconn-name-num Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User
where name is the system name of the Ascend unit (the name specified by the Name parameter in the System profile), and num is a number in a sequential series, starting with 1.
- On the second line, specify the User-Name attribute to indicate the name of the device to
which the user makes the nailed-up connection.
- Set Framed-Protocol=PPP.
- Set the Ascend-Call-Type attribute to Nailed or Nailed/Mpp.
- If the remote end is configured to wait for the MAX TNT to initiate FT1 calls, set
Ascend-FT1-Caller=FT1-Yes in the RADIUS user profile for the local MAX TNT. If the
remote end is configured to initiate FT1 calls, set Ascend-FT1-Caller=FT1-No in the user
profile for the local MAX TNT.
- Set the Ascend-Group attribute to specify the nailed-up channels the profile can use.
- As an option, set the Ascend-Backup attribute to the name of a backup profile.
Example of configuring a nailed-up connection
In Figure 4-8, the MAX TNT establishes a Nailed-up connection with another MAX TNT across the WAN.
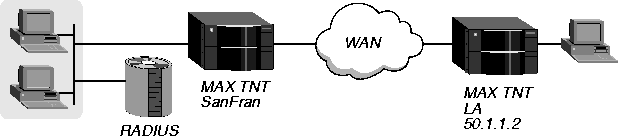
Figure 4-8. Configuring a nailed-up connection
To establish a nailed-up link between two MAX TNT units, and have the connection use the channels in group 1, you would configure the pseudo-user profile as follows:
permconn-SanFran-1 Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User
User-Name="LA",
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Framed-Address=50.1.1.2,
Framed-Netmask=255.0.0.0,
Ascend-Route-IP=Route-IP-Yes,
Ascend-Metric=7,
Framed-Routing=None,
Ascend-Idle-Limit=0,
Ascend-Call-Type=Nailed,
Ascend-Group="1",
Ascend-FT1-Caller=FT1-Yes
Managing bandwidth
You can manage bandwidth in the following ways:
How Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) works
The MAX TNT uses the time period specified by the Ascend-Seconds-Of-History attribute as the basis for calculating average line utilization (ALU), and uses the algorithm specified by the Ascend-History-Weigh-Type attribute for calculating ALU.
The MAX TNT then compares ALU to the percentage specified by the Ascend-Target-Util attribute. When ALU exceeds the threshold defined by Ascend-Target-Util for a time greater than the value of the Ascend-Add-Seconds attribute, the MAX TNT attempts to add the number of channels specified by the Ascend-Inc-Channel-Count attribute. When ALU falls below the threshold defined by Ascend-Target-Util for a time greater than the value of the Ascend-Remove-Seconds attribute, the MAX TNT attempts to remove the number of channels specified by the Ascend-Dec-Channel-Count attribute.
The MAX TNT compares the calculated ALU to the percentage specified in the Ascend-Target-Util attribute. It uses the following logic to determine when to add channels:
If ALU is greater than Ascend-Target-Util for more than Ascend-Add-Seconds seconds, add Ascend-Inc-Channel-Count channels.
The MAX TNT uses the following logic to determine when to subtract channels:
If ALU is less than Ascend-Target-Util for more than Ascend-Remove-Seconds seconds, subtract Ascend-Dec-Channel-Count channels.
How RADIUS authenticates multiple channels
When the system adds additional channels, the MAX TNT must authenticate each one. You can secure each circuit with one of the methods described in the following sections.
Static passwords
Before the MAX TNT dials a new circuit, it prompts the user to enter a static, reusable password as specified in the RADIUS user profile. To prevent intruders from capturing the password as it travels across the WAN, you can specify that the MAX TNT use the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). This protocol uses encryption to protect the password and verify the identity of the caller.
(For information about specifying a static password, see Specifying a password. For information about requiring CHAP authentication, see Specifying an access protocol for incoming calls.)
Tokens
Using PAP-Token authentication, RADIUS can require a user to specify a one-time-only password, generated by a token-card server, for each additional channel. This password is called a token. (For information, see Configuring PAP-Token authentication.)
Combination of static passwords and tokens
In RADIUS, you can indicate that the user need only specify a token for the initial channel, and that CHAP must authenticate all other channels. Whenever the MAX TNT uses PAP-Token-CHAP authentication and adds channels to a PPP or MP+ call, the calling unit sends the encrypted value of Aux-Send-Password (found in the Connection profile used to dial the call). The answering unit checks this password against the value of Ascend-Receive-Secret in the RADIUS user profile. The answering unit receives Ascend-Receive-Secret from the RADIUS server when the first channel of the call connects.
(For details, see Configuring PAP-Token-CHAP authentication.)
Cached tokens
By using Cache-Token authentication, you can configure RADIUS to reuse a token dynamically generated during session initiation. The token is transmitted by CHAP, and then cached for reuse. When the MAX TNT needs to add channels or make a new call, the MAX TNT uses the cached token to authenticate the additional bandwidth. You can specify a timeout value for the cached token, or configure the system to maintain the token throughout the session.
(For detailed information about setting up RADIUS for cached passwords, seeConfiguring Cache-Token authentication.)
Overview of DBA attributes
To configure DBA in RADIUS, use the attributes listed in Table 4-8.
Configuring DBA in RADIUS
To configure DBA for a RADIUS user profile, first configure an MP+ connection, as described in Setting up a dial-in PPP, MP, or MP+ connection. Then, perform the following steps. (For guidelines on how to set up DBA for optimum performance, see Guidelines for optimum use of DBA.)
- Set the Ascend-Target-Util attribute to the percentage of bandwidth use at which the MAX
TNT should add or subtract bandwidth.
- Set the Ascend-History-Weigh-Type attribute to the algorithm the MAX TNT should use
for calculating ALU.
- Set the Ascend-Seconds-of-History attribute to the number of seconds the MAX TNT
should use as a sample for calculating ALU.
- Set the Ascend-Add-Seconds attribute to the number of seconds that ALU must exceed the
Ascend-Target-Util threshold before the MAX TNT begins adding bandwidth to a session.
- Set the Ascend-Remove-Seconds attribute to the number of seconds that ALU must fall
below the Ascend-Target-Util threshold before the MAX TNT begins removing
bandwidth from a session.
- Set the Ascend-Base-Channel-Count attribute to specify the initial number of channels the
MAX TNT sets up when originating calls for the link.
- Set the Ascend-Maximum-Channels attribute to specify the maximum number of channels
allowed on a call.
- Set the Ascend-Minimum-Channels attribute to specify the minimum number of channels
the call maintains.
- Set the Ascend-Inc-Channel-Count attribute to specify the number of channels to add to a
call when increasing bandwidth.
- Set the Ascend-Dec-Channel-Count attribute to specify the number of channels to remove
from a call when decreasing bandwidth.
- Set the Ascend-DBA-Monitor attribute to specify how the MAX TNT monitors traffic on
an MP+ call.
Guidelines for optimum use of DBA
For optimum MP+ performance, both sides of a connection must set the base channel count, minimum channel count, and maximum channel count to the same number. In addition, the values for the Ascend-Seconds-Of-History, Ascend-Add-Seconds, and Ascend-Remove-Seconds attributes should smooth out spikes in bandwidth utilization that last for a shorter time than it takes to add capacity. Over T1 lines, the MAX TNT can add bandwidth in less than ten seconds. Over ISDN lines, the MAX TNT can add bandwidth in less than five seconds.
After the MAX TNT adds bandwidth, you typically incur a minimum usage charge. Thereafter, billing is time sensitive. The Ascend-Remove-Seconds value should be at least equal to the minimum duration charge plus one or two billing time increments. Typically, billing is done to the next multiple of six seconds, with a minimum charge for the first 30 seconds.
If you specify a small value for the Ascend-Seconds-Of-History attribute, and increase the values of the Ascend-Add-Seconds and Ascend-Remove-Seconds attributes, the system becomes less responsive to quick spikes. The easiest way to determine the proper values for all these attributes is to observe usage patterns.
Avoid adding or subtracting channels too quickly (less than 10-20 seconds apart). Adding or subtracting channels very quickly leads to many short duration calls, each of which incur the carrier's minimum charge. In addition, adding or subtracting channels too quickly can affect link efficiency, because the devices on either end have to retransmit data when the link speed changes.
When selecting a target utilization value, monitor how the application behaves when using different bandwidths and different loads. For example, an application might be able to use 88% of a 64-Kbps link, but only 70% of a 256-Kbps link.
Example of configuring DBA
In Figure 4-9, an incoming MP+ connection for the user John at IP address 200.0.5.1 uses DBA. The MAX TNT adds two channels if the bandwidth use exceeds 80% for more than 30 seconds, and remove two channels if the bandwidth use falls below 80% for more than 30 seconds. The MAX TNT monitors the traffic in both directions.
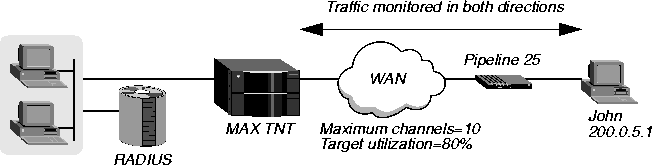
Figure 4-9. Configuring DBA
John's RADIUS user profile contains all the RADIUS attributes necessary for configuring DBA. In this example, you would configure John's RADIUS user profile as follows:
John Password="4yr66", User-Service=Framed-User
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Framed-Address=200.0.5.1,
Framed-Netmask=255.255.255.0,
Ascend-Target-Util=80,
Ascend-History-Weigh-Type=History-Constant,
Ascend-Seconds-Of-History=90,
Ascend-Add-Seconds=30,
Ascend-Remove-Seconds=30,
Ascend-Maximum-Channels=10,
Ascend-Inc-Channel-Count=2,
Ascend-Dec-Channel-Count=2,
Ascend-DBA-Monitor=DBA-Transmit-Recv
Configuring a time limit and idle connection attributes
To configure a time limit and idle connection values, use the attributes listed in Table 4-9.
Table 4-9. Time limit and idle connection attributes
Attribute
|
Specifies
|
Possible values
|
|---|
|
Ascend-Idle-Limit (244)
|
Number of seconds the MAX TNT waits before clearing a call when a session is inactive.
|
Number from 0 to 65535. If you specify 0 (zero), the MAX TNT always clears a call when a session is inactive. The default value is 120.
If you accept the default, and the Answer-Defaults profile specifies a value for the analogous Idle-Timer parameter, the MAX TNT ignores the Idle-Timer value and uses the Ascend-Idle-Limit default.
|
|
Ascend-Maximum-Call-Duration (125)
|
Maximum number of minutes an incoming call can remain connected. For a multichannel call, the value you specify applies to each individual channel, not to the connection as a whole.
|
Number from 0 to 1440. The default value is 0 (zero). If you accept the default, the MAX TNT does not set a limit on the duration of an incoming call.
|
|
Ascend-Maximum-Time (194)
|
Maximum length of time in seconds that any session is allowed. Once a session reaches the time limit, its connection is taken offline.
|
Number from 0 to 4,294,967,295. The default value is 0 (zero). When you accept the default, the MAX TNT does not enforce a time limit.
|
|
Ascend-MPP-Idle-Percent (254)
|
Percentage of bandwidth use below which the MAX TNT clears a single-channel MP+ call.
|
Number from 0 to 99. The default value is 0 (zero), which causes the MAX TNT to ignore bandwidth utilization when determining whether to clear a call.
|
|
Ascend-Preempt-Limit (245)
|
Number of idle seconds the MAX TNT waits before using one of the channels of an idle link for a new call.
|
Number from 0 to 65535. The MAX TNT never preempts a call if you enter 0 (zero). The default value is 60.
|
To specify the time limit for a session and the action the MAX TNT should take when a connection is idle, perform the following steps. (For guidelines on how to set up idle connection attributes for optimum performance, see Guidelines for optimum use of idle connection attributes.)
- Configure an MP+ connection, as described in Setting up a dial-in PPP, MP, or MP+
connection.
- Set the Ascend-Maximum-Call-Duration attribute to specify the number of minutes an
incoming call can remain connected. For a multichannel call, the value you specify applies
to each individual channel, not to the connection as a whole. The MAX TNT checks the
connection once per minute, so the actual time the call is connected is slightly longer than
the time you set.
- Set the Ascend-Maximum-Time attribute to specify the maximum length of time in
seconds that any session is allowed. Once a session reaches the time limit, its connection is
taken offline.
- Set the Ascend-Idle-Limit attribute to indicate the number of seconds the MAX TNT
waits before clearing a call when a session is inactive.
- Set the Ascend-MPP-Idle-Percent attribute to specify a percentage of bandwidth
utilization below which the MAX TNT clears a single-channel MP+ call. (Because the
Ascend-MPP-Idle-Percent attribute is dependent on traffic levels on both sides of the
connection, Ascend recommends that you use the Ascend-Idle-Limit attribute instead.)
- Set the Ascend-Preempt-Limit attribute to indicate the number of idle seconds the MAX
TNT waits before using one of the channels of an idle link for a new call.
Guidelines for optimum use of idle connection attributes
When you set the Ascend-MPP-Idle-Percent attribute, bandwidth utilization must fall below this percentage on both sides of the connection before the MAX TNT clears the call. If the device at the remote end of the link has an Ascend-MPP-Idle-Percent setting lower than the value you specify, the MAX TNT does not clear the call until bandwidth utilization falls below the lower percentage.
If the time set by the Ascend-Idle-Limit expires, the call disconnects whether or not bandwidth utilization falls below the Ascend-MPP-Idle-Percent setting. When bandwidth utilization falls below the Ascend-MPP-Idle-Percent setting, the call disconnects regardless of whether the time specified by the Ascend-Idle-Limit attribute has expired.
Example of configuring time limit and idle connection values
In Figure 4-10, an MP+ call from the user John at IP address 200.0.5.1 can remain connected for a maximum of 10 minutes.
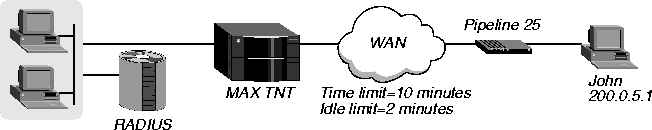
Figure 4-10. Configuring time limit and idle connection values
The MAX TNT clears the call when the session is inactive for more than two minutes. In this example, you would configure John's user profile as follows:
John Password="4yr66", User-Service=Framed-User
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Framed-Address=200.0.5.1,
Framed-Netmask=255.255.255.0,
Ascend-Maximum-Call-Duration=10,
Ascend-Idle-Limit=120
Limiting access to devices and services
To limit the devices and services a PPP, MP, or MP+ link can use, you must specify a value for each of the attributes listed in Table 4-10. If you do not specify a value, the MAX TNT does not restrict the devices and services available to the caller.
To limit access to devices and services for a PPP, MP, or MP+ connection, perform the following steps. The steps assume you have already set the User-Name and Password attributes, and any other appropriate PPP, MP, or MP+ attributes.
- Set the User-Service=Framed-User attribute on the first line of the profile.
If RADIUS authenticates an incoming call with the User-Name and Password attributes, and the type of call matches the value of the User-Service attribute, the MAX TNT applies the attributes specified in the user profile. If the type of call does not match the value of the User-Service attribute, the MAX TNT rejects the call.
- To specify the phone number of the device the caller can access, set Client-Port-DNIS.
- To restrict users to an ISDN or modem connection, set the NAS-Port-Type attribute.
- To specify whether the MAX TNT uses only the 56-Kbps portion of a channel, even when
all 64 Kbps appear to be available, set the Ascend-Force-56 attribute.
Example of restricting service access
In Figure 4-11, a Pipeline 25 is the calling device. The connection can use PPP protocols (PPP, MP+, or MP) and IP routing, but the caller has no access to the terminal server.
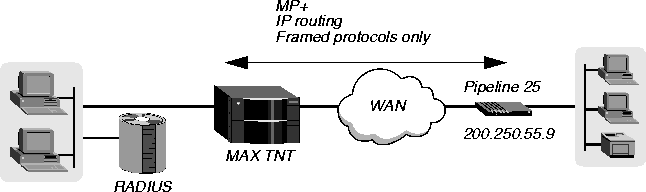
Figure 4-11. Restricting service access
In this example, you would configure the user profile as follows:
Ascend Password="Pipeline", User-Service=Framed-User
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Framed-Address=200.250.55.9,
Framed-Netmask=255.255.255.248,
Ascend-Link-Compression=Link-Comp-Stac,
Framed-Compression=Van-Jacobson-TCP-IP,
Ascend-Route-IP=Route-IP-Yes,
Ascend-Metric=2
Example of configuring unrestricted access
In Figure 4-12, both framed and unframed users can dial into the MAX TNT. IP and IPX routing are both enabled.
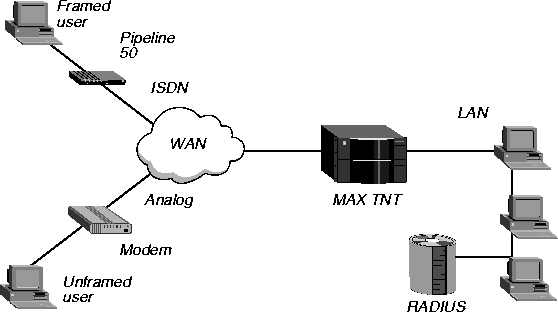
Figure 4-12. Configuring unrestricted access
Allowing both framed and unframed users to dial in requires a setting of Auth-Send67=No in the External-Auth profile's Rad-Auth-Client subprofile, and the RADIUS user profile must not include the User-Service attribute. In this example, you would configure the RADIUS user profile as follows:
FM Password "ACE"
Ascend-Idle-Limit=0,
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Ascend-Assign-IP-Pool=1,
Ascend-Route-IPX=Route-IPX-Yes,
Ascend-IPX-Peer-Mode=IPX-Peer-Dialin
Restricting access to ports, lines, and channels
If you want to restrict the ports, lines, and channels that a user can access on a PPP, MP, or MP+ call, set the NAS-Port attribute. On the first line of the user profile, specify the network port on which the MAX TNT must receive the call. The format you use for NAS-Port depends upon the setting of the New-NAS-Port-ID-Format parameter in the System profile.
When New-NAS-Port-ID-Format=Yes
When New-NAS-Port-ID-Format=Yes, use the following format for the NAS-Port value:
shelf slot line channel
where shelf specifies the shelf number (0-3), slot specifies the slot number (0-15), line specifies the line number (0-31), and channel specifies the channel number (0-31) for an ISDN call. For an analog call, the values are the same, except that line number can be 0-63, and the channel number is always 1. The default value for the RADIUS daemon appears in the /etc/services file.
Specify a decimal value. The value must translate to a bit-encoded number that specifies the shelf, slot, line, or channel. For an ISDN call, the bit-encoded number has the following format:
- The shelf number is composed of two bits.
- The slot number is composed of four bits.
- The line and channel numbers are each composed of five bits.
For an analog call, the bit-encoded number has the following format:
- The shelf number is composed of two bits.
- The slot number is composed of four bits.
- The line number is composed of six bits.
- The channel number is composed of four bits.
When New-NAS-Port-ID-Format=No
When New-NAS-Port-ID-Format=No, use the following format for the NAS-Port value:
tllcc
where t indicates 1 for a digital call or 2 for an analog call, ll indicates the line number, and cc indicates the channel number.
Example of restricting access to ports, lines, and channels
The following example shows how you would specify the NAS-Port setting on the first line of a user profile to restrict an ISDN user to channel 2 on line 2 of slot 2, shelf 1:
Robin Password="password", NAS-Port=1057
User-Service=Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Ascend-Assign-IP-Pool=1,
Ascend-Route-IP=1,
Ascend-Idle-Limit=300,
Framed-Routing=None
The NAS-Port value of 1057 translates to the bit-encoded number 0000010000100001. This number indicates the following NAS port:
shelf=00 (shelf 1)
slot=0001 (shelf 2)
line=00001 (line 2)
channel=00001 (channel 2)
Setting up disconnects
If you write a special RADIUS client program to disconnect a link, the MAX TNT can accept RADIUS requests from clients to disconnect a link for a particular session, user, or IP address. The following sections describe how to configure a disconnect request.
Overview of disconnect-request attributes
A RADIUS Disconnect-Request packet (code 40) contains the attributes necessary for making a disconnect request. Table 4-11 lists the attributes.
The MAX TNT sends the session key and session ID in all RADIUS access requests. You can also obtain the session key, session ID, and user name through RADIUS accounting or from the accounting MIB (for systems that support SNMP accounting). If the MAX TNT assigns the IP address from a pool, RADIUS accounting or the accounting MIB can provide the address as well.
The Auth-Session-Key and Auth-Attribute-Type parameters in the External-Auth profile's Rad-Auth-Server subprofile determine the attributes the MAX TNT uses when handling the disconnect request. For complete information about setting these parameters, see Specifying session key parameters.
Configuring attributes for disconnect requests
To set up a RADIUS user profile that requests a disconnect, follow the steps described below. Only the first step is required. All others are optional, and depend upon the needs of your site. None of the attributes may appear more than once. That is, you may not specify two different user names with a single request.
- Specify the values for the User-Name and Password attributes. These attributes must
identify a user at the IP address indicated by the Auth-Client or Auth-Netmask parameters
in the External-Auth profile's Rad-Auth-Server subprofile.
- To identify the session by IP address, set the Framed-Address attribute.
- To identify the session by its ID number, set the Acct-Session-Id attribute. The number
you specify must match the session reference number used in SNMP accounting or
RADIUS accounting.
- To identify the session by a session key, set the Ascend-Session-Svr-Key attribute.
How the MAX TNT handles disconnect requests
The MAX TNT silently discards a Disconnect-Request packet if one of the following conditions is true:
- The packet is badly formatted.
- The client is not on the list of clients allowed to send RADIUS requests to the server.
- The authenticator field is incorrect.
- The packet contains invalid attribute values.
If RADIUS finds at least one session it can disconnect, the response code is 41 (Disconnect-Request-ACK). Otherwise, the code is 42 (Disconnect-Request-NAK). RADIUS does not return any attributes in the response.
Example of configuring disconnects
If two users with the name Steve are logged into the MAX TNT, a request specifying the name Steve disconnects both. A request specifying the session reference number of the first user disconnects only that user.
If there is a four-channel MP session for user Steve at IP address 11.0.0.1, a request specifying IP address 11.0.0.1 and/or the name Steve disconnects all four channels. A request specifying the session reference number associated with one of the four channels disconnects all channels in the MP session. If the request specifies Steve and an address of 11.0.0.2, the MAX TNT returns a NAK because there is no session Steve with that address.
If there is also a terminal-server session for Steve in addition to the four-channel MP session, a request specifying Steve disconnects both. A request specifying Steve and 11.0.0.1 disconnects only the MP session. Likewise, a request specifying 11.0.0.1 disconnects only the MP session.
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


techpubs@eng.ascend.com
Copyright © 1998, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights
reserved.

