
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


Configuring IDSL Cards
This chapter covers the following topics:
Introduction
Note: The MAX TNT must have software version 1.3Ai2 or later to support IDSL. Refer to
the MAX TNT release notes for information about obtaining and loading MAX TNT software.
IDSL is part of a broad range of Ascend MultiDSL offerings that let you implement DSL technologies immediately. Because IDSL uses the same 2B1Q signalling used by ISDN, existing ISDN U-interface devices-such as terminal adapters (TAs) or Ascend Pipelines-can connect to a MAX TNT with an IDSL line card without modification.
IDSL supports high-bandwidth applications such as remote access, Internet or intranet access, and telecommuting. This integrated solution provides centralized line terminations to single-pair copper wires for transmission of full duplex data at 128 Kbps and at distances of up to 18,000 feet.
The IDSL MAX TNT provides a separate, data-only network that does not congest the "voice network" with data traffic. In this way, the MAX TNT replaces a switch for data traffic. The IDSL line card also provides some of the functionality of a switch for monitoring line quality and troubleshooting the line. As subscriber requirements change, you can use the same platform to add other MultiDSL technologies such as SDSL and ADSL.
By installing the IDSL line card into the MAX TNT, you can cost-effectively support a wide range of analog, ISDN, Frame Relay and IDSL services on a single, manageable platform.
The IDSL line card provides the following features:
- ISDN BRI (2B1Q) signalling
- 2 DB37 connectors, each providing 16 IDSL sessions for a total of 32 sessions
- 128Kbps user bit rate over a two-wire subscriber loop
- Line Termination (LT) mode
- No switch required
- Data calls only
- Point-to-point
- Support for both switched channels and nailed channels (including Ascend's SuperDigital 128)
- Support for maintenance functions including BRI-U interface monitoring commands, loopback, and out-of-band management
Installing the IDSL card
The IDSL card is illustrated in Figure 12-1. Note that the IDSL card is double-height, meaning it occupies two slots in the MAX TNT.
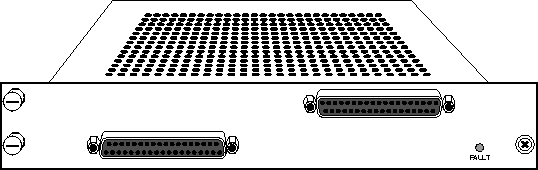
Figure 12-1. MAX TNT IDSL card
You install IDSL cards in the same way you install other MAX TNT slot cards. For instructions, see Installing a slot card.
Connecting the MAX TNT IDSL line
The MAX TNT IDSL card ships with a dual 50-pin telco to triple-DB37 cable (part number 2510-0311-xxx, where xxx represents digits subject to change). This cable allows you to efficiently use all the ports on a 50-pin telco connector. Because each IDSL card has 32 ports, you need two DB37 connectors and two 50-pin telco connectors (each of which support up to 24 ports) to accommodate all the ports on the IDSL card. This leaves the second telco connector underutilized. The third DB37 connector is designed to be attached to a second IDSL card, thus bringing a total of 48 ports from the DB37 connectors to the 50-pin telco connectors. Figure 12-2 illustrates the recommended use of the IDSL cable.
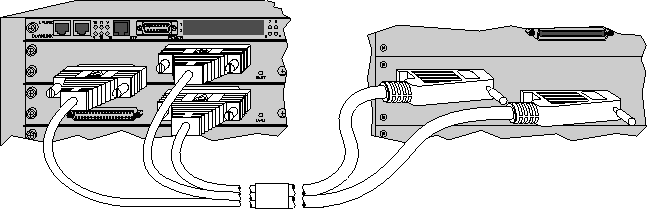
Figure 12-2. Connecting your IDSL line
Example of IDSL configuration
In Figure 12-3, a Pipeline connects, over an MPP connection, a single user to a MAX TNT with an IDSL line card installed. The user has a permanent connection to the MAX TNT, with 128Kbps bandwidth. This example uses an Ascend Pipeline, but you can configure any ISDN U-interface device, such as a terminal adapter (TA), similarly.
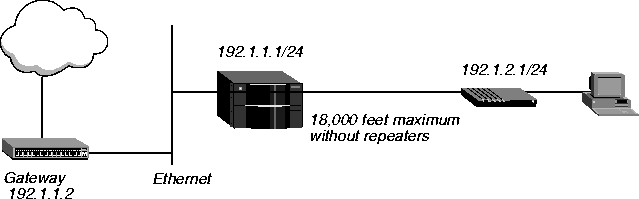
Figure 12-3. Single IDSL user with a Pipeline
Configuring the MAX TNT
This example assumes the MAX TNT has already been configured with the following information:
- IP address of 192.1.1 4/24
- System name of
idsltnt
Configuring the MAX TNT for this example involves these general steps:
Configuring the IDSL profile
To configure the MAX TNT IDSL profile
- Read in the IDSL profile.
admin> read idsl {1 11 1}
- List the contents of the first line interface profile:
admin> list line-interface 1
- Make sure the line is enabled (the default):
admin> set enabled=yes
- Specify a switched connection (the default):
admin> set channel-usage = switched-channel
- Write the profile:
admin> write
Configuring a Connection profile for the remote device
To configure a Connection profile for the remote device:
- Create a Connection profile for the Pipeline:
admin> new connection pipeline
- Activate the profile:
admin> set active=yes
- Set the encapsulation:
admin> set encapsulation-protcol=mpp
- Set the dial number:
admin> set dial-number=5551212
Note that the Dial Number is not a true telephone number. Dialing this number through the public telephone network would not reach the Pipeline. However, the MAX TNT can use the Dial number to identify and route incoming calls from the Pipeline.
- List the IP-Options profile:
admin> list ip-options
- Enable IP routing for this Connection profile:
admin> set ip-routing-enabled=yes
- Specify the Pipeline IP address:
admin> set remote-address=192.1.2.1/24
- Set the encapsulation:
admin> set encapsulation-protocol=mpp
- List the Telco options profile:
admin> list.. telco-options
- Set the data service:
admin> set data-service=64K-clear
- Set the call type:
admin> set call-type=off
This specifies that nailed calls are not used.
- Set the idle timer to keep the connection for timing out due to inactivity
admin> list.. session-options
admin> set idle-timer=0
- Write the Connection profile:
admin> write
Configuring a static route to the gateway
To configure a static route to the gateway:
- Read in the IP-Route Default profile:
admin> read ip-route default
- Enter the address of the Gateway on the local LAN to the remote network.
set gateway-address = 192.1.1.2
- Write the profile:
admin> write
Configuring the Pipeline
Note: When configuring a remote ISDN device to attach to the IDSL line card, always select
ATT 5ESS Point-to-Point as the switch type. The IDSL line card can only emulate the ATT
5ESS Point-to-Point switch.
Before you configure the Pipeline, make sure the PC connected to the Pipeline has an IP address on the same subnet as the Pipeline, and that the IP address of the Pipeline is configured as the default gateway for the PC.
To configure the Pipeline:
- From the Main Edit menu, select Configure.
- Specify the following values:
Switch Type=AT&T/P-T-P
Chan Usage=Switch/Switch
My Name=pipeline
My Addr=192.1.2.1/24
Rem Name=idsltnt
Rem Addr=192.1.1.1/24
Route=IP
- Exit and save the Configure profile.
- From the Main Edit menu, select Ethernet > Connections > IDSLTNT Connection profile.
- Specify the following values:
Active=Yes
Encaps=MPP
Dial #=5551213
Route IP=Yes
- Open the Encaps Options submenu.
- Specify the following values:
Base Ch Count=2
Min Ch Count=2
Max Ch Count=2
These values force the Pipeline to use two 64K channels.
- Open the Session Options submenu.
- Set
Idle=0
This prevents the connection from timing out due to inactivity.
- Open the Telco Options submenu.
Specify the following values:
Call Type=Switched
Data Svc=64K
- Exit and save the Connection profile.
Configuring a nailed IDSL connection
You can configure only one channel on an IDSL line for nailed usage. The Channel-Usage parameter specifies the usage for the channel. It can be one of the following values:
- Unused-Channel. Channel is unused. Send the single idle code defined for this channel.
- Switched-Channel (the default). Switched channel.
- Nailed-64-Channel. A clear-channel 64K circuit. Does not require any setup information.
You must also assign that channel a group number using the Nailed-Group parameter. The Connection profile for the remote device then references the assigned group number in its Nailed-Group setting, to direct the connection to use the IDSL nailed channel.
The following example shows how to configure a nailed channel on the first channel of line 18 of an IDSL card in shelf 1, slot 7:
admin> read idsl {1 7 18}
IDSL/{ shelf-1 slot-7 18 } read
admin> set line enabled = yes
admin> list line channel 1
channel-usage = switched-channel
nailed-group = 0
admin> set channel-usage = nailed
admin> set nailed-group = 10
admin> write
IDSL/{ shelf-1 slot-7 18 } written
![[Top]](../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../images/index.jpg)


techpubs@eng.ascend.com
Copyright © 1997, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights
reserved.

