
This chapter covers the following topics:
Introduction to E1
An E1 line supports 32 64-Kbps channels, each of which may be used to transmit and receive data or digitized voice. The line uses framing and signaling to achieve synchronous and reliable transmission. The most common configurations for E1 lines are PRI and unchannelized. (For information about provisioning your E1 line for use with the MAX TNT, see Appendix A, "Provisioning the Switch. ")
ISDN Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
In Europe, an E1/PRI line typically supports 30 B channels and one D channel. But if NFAS signaling is in use, more than one ISDN PRI line on a single card can share a single D channel. PRI configurations are used to receive multiple, simultaneous ISDN calls from analog-modem and digital-services dial-in traffic. Another common use of E1/PRI line is to connect a PBX (Private Branch Exchange) to a central office switch. Nailed or unchannelized E1
An unchannelized E1 line may be used for nailed connections such as to a Frame Relay network. In such cases the configuration is static, and the MAX TNT treats the E1 line as if it were a single connection at a fixed speed, without individual channels.
Installing the E1 card
You install E1 cards in the same way you install other MAX TNT slot cards. For instructions, see Installing a slot card.
Connecting the MAX TNT E1 line to the WAN
When connecting your E1 line, keep the following points in mind:
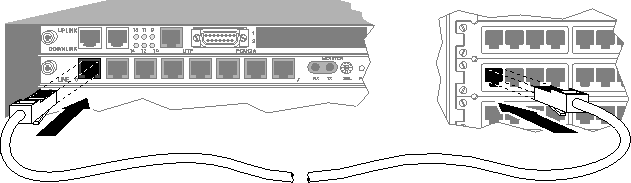
Figure 8-1. Connecting your E1 line
Monitoring the E1 line with bantam jacks
Each E1 card provides transmit and receive bantam jacks to monitor the status of the E1 lines. The Tx line carries what the MAX TNT transmits to the network. The Rx line carries what the MAX TNT receives from the network. The bantam jacks do not interfere with the signal either coming into or going out of the MAX TNT.
Overview of E1 configuration
Table 8-1 lists the sections describing common tasks you might have to perform to configure an E1 line. The table includes a brief description of each task, and lists the parameters you will use.
For complete information about the associated parameters, see the MAX TNT Reference Guide.
Understanding configuration requirements
You need the following information from your E1/PRI service provider:
Making a profile the working profile
When the MAX TNT system detects that E1 card has been installed, it creates a default E1 profile for each of the eight lines on the card.
admin> dir e1By default, a line is not enabled, which means that it is not available for use. Its default signaling method is inband, typically used for channelized connections.
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 2 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 4 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 5 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 6 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 7 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 8 }
320 12/20/1996 20:55:31 { shelf-1 slot-2 3 }
317 01/08/1997 09:58:55 { shelf-1 slot-2 1 }
To configure an E1 profile, make it the working profile by reading it into the edit buffer. For example:
admin> read e1 {1 2 1}
E1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
Once you have read in a profile, it remains the working profile until you read in another profile. To save your configuration changes, use the write command. For example,
admin> writeTo list the parameters in an E1 profile, use the List command, as in the following example:
E1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1} written
admin> listThe following example shows the parameters in an E1 profile, with sample settings:
physical-address* = { shelf-1 slot-2 1 }
line-interface = { yes esf b8zs eligible middle-priority isdn wink-star+
E1 { shelf-N slot-N N }
physical-address* = { shelf-N slot-N N }
back-to-back = false
line-interface
enabled = yes
t-online-type = none
t302-timer = 1500
frame-type = g703
clock-source = eligible
clock-priority = middle-priority
signaling-mode = isdn
default-call-type = digital
switch-type = net5-pri
front-end-type = short-haul
channel-config = [ { unused-channel 9 "" { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 } { switche+
layer3-end = x-side
layer2-end = b-side
nl-value = 64
loop-avoidance = 7
number-complete = end-of-pulsing
group-b-signal = signal-b-6
group-ii-signal = signal-ii-2
answer-delay = 200
caller-id = no-caller-id
channel-config N
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
Assigning a name to E1 line profiles
In an E1 profile, the Name parameter enables you to assign the profile a name. The name can include up to 16 characters. After you assign it, it is displayed after the line's physical address in the Dir command output. For example:
admin> read e1 {1 12 0}
admin> set name = E1 Trunk
admin> write
E1/{ shelf-1 slot-12 0 } written
admin> dir e1
17 04/17/1997 19:00:02 { shelf-1 slot-12 0 } "E1 Trunk"
For E1 lines, the Line Status window displays either the name (if assigned) or the physical address. If the name is longer than eight characters, the last character displayed is a plus-sign (+).
Enabling a line
By default each E1 line is disabled. To enable an E1 line, read its profile to make it the working profile, then set enable to Yes, as in the following example:
admin> read e1 {1 2 1}
E1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
admin> set line enabled = yes
admin> write
E1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } written
Configuring a back-to-back connection
For diagnostics, you can configure DASS-2 or DPNSS lines in a back-to-back connection. A crossover cable connects an E1 port of one MAX TNT to an E1 port of another MAX TNT. No switch is required, and the connection is entirely local. One MAX TNT should be set up for DTE operation, and the other for DCE operation.
admin> write
Specifying the framing
The E1 framing mode may be the G703 (the standard framing mode used by most E1 ISDN and DASS2 providers), 2DS (a variant of G.703 required by most E1 DPNSS providers in the U.K). If the line is not configured for ISDN signaling, you can use the D4 format, also known as the superframe.
admin> set line frame-type = [G703|2DS|D4|ESF]
admin> write
Specifying E1 signaling
An E1 line's signaling mode can be any of the following:
admin> set line signaling-mode = signalingmode
admin> write
Configuring ISDN PRI signaling
For ISDN signaling you must also specify the type of switch providing E1/PRI service to your MAX TNT. Obtain the information from your ISDN carrier.
admin> set line frame-type = esfTo see a complete list of switch types supported on the MAX TNT, refer to the MAX TNT online help or the MAX TNT Reference Guide.
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn
admin> set line switch-type = switchtype
admin> set line channel 17 channel-usage=d-channel
admin> write
Configuring R2 signaling
R2 signaling is an ITU-T standardized signaling protocol, which can be used on E1 digital trunks for switched circuits. It uses a combination of A/B bit manipulation, in channel 16 of the E1 frame (line signaling), and in-band MF tone generation and detection (register signaling). The relevant specifications are in ITU-T recommendations Q.400 to Q.490. R2 signaling is widely implemented in international markets where ISDN PRI is not yet available. The default bandwidth for data calls coming in over E1 channels using R2 signaling is 64K.
admin> read e1 {1 2 2}
e1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 2 } read
admin> set line enabled = yes
admin> set line frame-type = 2DS
admin> set line signaling-mode = e1-r2-signaling
admin> set line switch-type = switch-cas
admin> set line number-complete = end-of-pulsing
admin> set line group-b-signal = signal-b-6
admin> set line group-ii-signal = signal-ii-2
admin> set line answer-delay = 200
admin> set line caller-id = get-caller-id
admin> write
Configuring DPNSS signaling
When you are connecting to a DASS 2 or DPNSS switch, you must set the following parameters:
In the following example, an administrator configures DPNSS signaling using a Mercury switch (a variant of DPNSS). The 2DS framing mode is specified-this mode gives a variant of G.703 required by most E1 DPNSS providers in the U.K. To configure an E1 line for DPNSS signaling, proceed as in the following example:
admin> set enabled = yes
admin> set signaling-mode = e1-dpnss-signaling
admin> set switch = mercury-dpnss
admin> set frame-type = 2ds
admin> set layer3-end = x-side
admin> set layer2-end = b-side
admin> set nl-value = 64
admin> set loop-avoidance = 7
admin> write
Configuring clocking
You can configure the MAX TNT to use any of the E1 lines as a master clock source for synchronous connections for an entire multishelf system. In synchronous transmission, both the sending device and the receiving device must maintain synchronization in order to determine where one block of data ends and the next begins.
admin> set clock-source = eligible
admin> set clock-priority = high-priority
admin> write
Configuring the front end E1 transceiver
The front-end type of the E1 transceiver may be short haul or long haul. Long haul is only for lines using 120 Ohm termination.
admin> set front-end-type=[short-haul|long-haul]
admin> write
Configuring channel usage
You must specify how each of the 32 channels of an E1 line is to be used. By default, E1 channels are configured as switched. Each of the 32 channels of an E1 line may be configured for one of the following uses:
admin> list line-interface
admin> set channel 1 channel-usage=[unused-channel|switched-channel |nailed-64-channel|d-channel]admin> write
Assigning phone numbers to switched channels
Assigning phone number to switched E1 channels is no different that assigning them to switched T1 channels. See Assigning phone numbers to switched channels.
Configuring trunk groups
Like nailed channels that have been assigned a group number, switched channels in a trunk group can be referenced from a Connection profile and Call-Route profile to direct outbound calls to use that specific bandwidth. Trunk groups also serve a variety of other purposes, such as separating lines supplied by different carriers so those lines can be used as backup for each other if one switch becomes unavailable. The decision to use trunk groups is a global one. Once you have enabled the use of trunk groups, every switched channels must be assigned a trunk group number or it will not be available for outbound calls.
admin> read system
SYSTEM read
admin> listThen assign the channels of each E1 line to a trunk group, as in the following example:
name = ""
system-rmt-mgmt = yes
use-trunk-groups = no
idle-logout = 0
parallel-dialing = 2
single-file-incoming = yes
analog-encoding = a-law
sessionid-base = 0
admin> set use-trunk-groups = yes
admin> write
admin> list line channel 1Note: Command history is very useful for repeating commands. Press the Up-Arrow key to redisplay the command, and then press Enter. (For more information, see The Ascend Command Line Interface.)
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set trunk-group = 4
admin> list .. 2
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set trunk-group = 4
admin> list .. 3
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set trunk-group = 4
admin> write
Configuring nailed channels
The number of nailed channels must be the same at both ends of the connection. For example, if there are 5 nailed channels at the local end, there must be 5 nailed channels at the remote end. However, channel assignments do not have to match. For example, Channel 1 may be switched at the local end and nailed at the remote end. Channels in a nailed group must be contiguous on the E1 line.
admin> list line channel 1
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set channel = nailed
admin> set nailed = 3
admin> list .. 2
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set channel = nailed
admin> set nailed = 3
admin> write
Specifying analog encoding for MAX TNT codecs
Codecs connected to T1 use a different encoding standard for digitized analog data than codecs connected to E1. The default for T1 is U-Law, the default for E1 is A-Law.
admin> read system
admin> set analog-encoding = a-law
admin> write
SYSTEM written
Default Call-Route profiles
When the MAX TNT system detects that an E1 card has been installed, it creates one default Call-Route profile associated with the card. For example:
admin> dir call-rThis default Call-Route profile routes outbound trunk calls to any line on the card. To handle inbound modem and LAN-session traffic, you should configure specific call routes. For details, see Chapter 15, "Call Routing in the MAX TNT."
9 12/11/1996 15:58:08 { { { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 } 0 }
13 01/06/1997 17:17:10 { { { shelf-1 slot-2 0 } 0 } 0 }
Copyright © 1997, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights reserved.