
Setting Up IPX Routing for WAN Links
Before you begin
Before you set up IPX routing for WAN links, you must perform some preliminary tasks at the MAX TNT configuration interface and in RADIUS. Preliminary MAX TNT tasks
The first task that you carry out at the MAX TNT configuration interface is required for all configurations. The others depend upon the type of configuration you plan to set up. Setting up the MAX TNT as an IPX router
Before you set up an IPX routing connection in RADIUS, you must set up the MAX TNT as an IPX router by configuring parameters in the IPX-Global, IPX-Interface, and Answer-Defaults profiles. For detailed information, see the MAX TNT Network Configuration Guide. Specifying an authentication protocol
If you set up a RADIUS user profile that enables IPX routing (but not IP routing), you must specify an authentication protocol for name and password authentication of PPP, MP, and MP+ calls. In the Answer-Defaults profile's PPP-Answer subprofile, set the Receive-Auth-Mode parameter to PAP-PPP-Auth, CHAP-PPP-Auth, MS-CHAP-PPP-Auth, or Any-PPP-Auth. (For descriptions of these settings, see Table 3-5.)
Unlike an IP routing configuration, in which the MAX TNT uniquely identifies the calling device by its IP address, an IPX routing configuration does not include a built-in way to uniquely identify callers. For this reason, you must use PAP, CHAP, or MS-CHAP password authentication, unless you configure IP routing in the same RADIUS user profile.
Specifying a network number for dial-in clients
Dial-in clients do not belong to an IPX network, so you must assign them an IPX network number. When you do so, a dial-in client can establish a routing connection with the MAX TNT. To provide an IPX network number, you must define a virtual IPX network by means of the IPX-Dialin-Pool parameter. The MAX TNT advertises the route to this virtual network and assigns it as the network address for dial-in clients. If the client does not supply its own unique node number, the MAX TNT assigns a unique node number as well. Preliminary RADIUS tasks
Before you set IPX attributes, you must configure a RADIUS user profile containing:
Introducing IPX routing
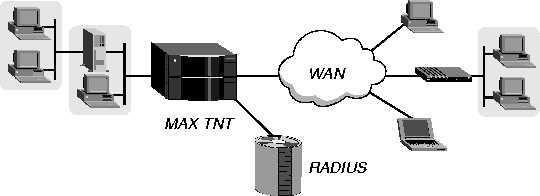
A MAX TNT configured for IPX routing enables NetWare clients and distributed Novell networks to use NetWare services across the WAN. Figure 10-1 shows a MAX TNT that routes IPX between WAN interfaces (connections) and a local Novell network.
Figure 10-1. Routing IPX between LAN and WAN interfaces
Overview of IPX-routing configuration tasks
You can carry out the following IPX configuration tasks:
Setting up IPX routing in a user profile
Table 10-2 lists the attributes relevant to IPX routing for a WAN connection.
To set up IPX routing in a RADIUS user profile:
Figure 10-2. A connection with NetWare servers on both sides
Server-2 Password="m2dan", User-Service=Framed-User
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Ascend-Route-IPX=Route-IPX-Yes,
Ascend-IPX-Peer-Mode=IPX-Peer-Router
Figure 10-3. A dial-in NetWare client requiring dynamic IPX network assignment
NetWareClient1 Password="m2dan", User-Service=Framed-User
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Ascend-Route-IPX=Route-IPX-Yes,
Ascend-IPX-Peer-Mode=IPX-Peer-Dialin
Setting up static IPX routes
To create static IPX routes, you configure a pseudo-user profile containing the route specifications. Each static IPX route contains all the information necessary to reach one NetWare server on a remote network. When the MAX TNT receives an outbound packet for that server, it finds the corresponding RADIUS user profile and dials the connection. You do not need to create an IPX route to a server that resides on the local Ethernet network. Recommended configurations
Most sites configure only a few IPX routes and rely on IPX RIP for most other connections. If you have servers on both sides of the WAN connection, Ascend recommends that you define a static route to the remote site even if your environment requires dynamic routes. If you have one static route to a remote site, it should specify a master NetWare server that knows about many other services. NetWare workstations can then learn about other remote services by connecting to that remote NetWare server. If the MAX TNT does not receive IPX RIP broadcasts from a remote unit, you should configure a static route to at least one server on the remote network. Configuring static IPX routes in a pseudo-user profile
To set up static IPX routes in a RADIUS pseudo-user profile, you must perform the following tasks:
For a unit-specific IPX dialout route, specify the first line of a pseudo-user profile in the following format:
ipxroute-name-num Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-UserFor a global IPX dialout route, specify the first line of a pseudo-user profile in the following format:
ipxroute-num Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-UserThe name argument is the system name of the MAX TNT (the name specified by the Name parameter in the System profile), and num is a number in a sequential series, starting at 1.
Ascend-IPX-Route="profile_name network# [node#] [socket#] [server_type] [hop_count] [tick_count] [server_name]"The MAX TNT fetches information from each pseudo-user profile in order to gather routing information. Table 10-3 describes each Ascend-IPX-Route argument.
How the MAX TNT adds IPX dialout routes to the routing table
Whenever you power on or reset the MAX TNT, RADIUS adds IPX dialout routes to the routing table as follows:
ipxroute-name-1, where name is the
system name.
ipxroute-num.
Figure 10-4. Using a static IPX route
ipxroute-CA-1 Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-UserHere is an example of how to define a global IPX route to Server-1:
Ascend-IPX-Route="Emma 9999ABFF 000000000002 0451 0004 2 10 Server-1"
ipxroute-1 Password="ascend", User-Service=Dialout-Framed-User
Ascend-IPX-Route="Emma 9999ABFF 000000000002 0451 0004 2 10 Server-1"
Copyright © 1998, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights reserved.